We earn commission when you buy through affiliate links.
This does not influence our reviews or recommendations.Learn more.
Even though Linux-based systems are often considered impenetrable, there are still risks that need to be taken seriously.

No matter the operating system, taking security measures is a must for servers.
Fortunately, there are tools available for a low price or for free that can help with this process.
They can detect flaws in different sections of a Linux based server.

Lynis
Lynisis a renowned security tool and a preferred option for experts in Linux.
It also works on systems based on Unix and macOS.
It is an open-source software app that has been used since 2007 under a GPL license.

Lynis is capable of detecting security holes and configuration flaws.
But it goes beyond that: instead of just exposing the vulnerabilities, it suggests corrective actions.
Thats why, to get detailed auditing reports, it is necessary to run it on the host system.

Installation is not necessary for using Lynis.
you’re free to extract it from a downloaded package or a tarball and run it.
Lynis was created by the original author of Rkhunter, Michael Boelen.

It has two types of services based on individuals and enterprises.
In either case, it has an outstanding performance.
Rootkits are a jot down of malicious software that can give server access to an unauthorized user.

If you are running a Linux-based server, rootkits can be a problem.
chkrootkit is one of the most used Unix-based programs that can detect rootkits.
It uses strings and grep (Linux tool commands) to detect issues.

Rkhunter
Developer Micheal Boelen was the person behind makingRkhunter(Rootkit Hunter) in 2003.
It is a suitable tool for POSIX systems and can help with the detection of rootkits and other vulnerabilities.
It also serves significantly as a server-side scanner.

The tool was initially developed especially for Unix.
It allows for command-line scanning, and it has a multi-threaded scalable demon to improve its scanning speed.
It can go through different kinds of files to detect vulnerabilities.

LMD doesnt limit itself to its own signature database.
It can leverage ClamAV and Team Cymrus databases to find even more viruses.
To populate its database, LMD captures threat data from connection edge intrusion detection systems.

LMD can be used through the maldet command line.
The tool is specially made for Linux platforms and can easily search through Linux servers.
It can detect malformed binaries, giving the user the tools to manage them, and neutralizing potential threats.
It utilizes sdb, which is a NoSQL database.
Software security researchers and software developers prefer this tool for its excellent data presentation ability.
It is recommended for any bang out of research on binary data.
It is designed for businesses of all sizes, helping them detect security issues hidden within their infrastructures.
As of June 2016, it had more than 47,000 NVTs.
Security experts use OpenVAS because of its ability to scan fast.
It also features excellent configurability.
OpenVAS programs can be used from a self-contained virtual machine for doing safe malware research.
Its source code is available under a GNU GPL license.
REMnux
REMnuxuses reverse-engineering methods for analyzing malware.
It can detect many web client-based issues, hidden in JavaScript obfuscated code snippets and Flash applets.
It is also capable of scanning PDF files and performing memory forensics.
It is effective due to its decoding and reverse-engineering capabilities.
Tiger
In 1992, Texas A&M University started working onTigerto increase their campus computers security.
Now, it is a popular program for Unix-like platforms.
The tool is free to use under a GPL license.
Tiger is entirely written on shell language thats one of the reasons for its effectiveness.
It performs that task by comparing the traffic sources with blacklisted sites published online.
Besides checking for blacklisted sites, It also uses advanced heuristic mechanisms for detecting different kinds of threats.
The detection system verifies if the traffic is good enough to exchange data between a server and the source.
YARA does have some extra features, but you need the OpenSSL library to use them.
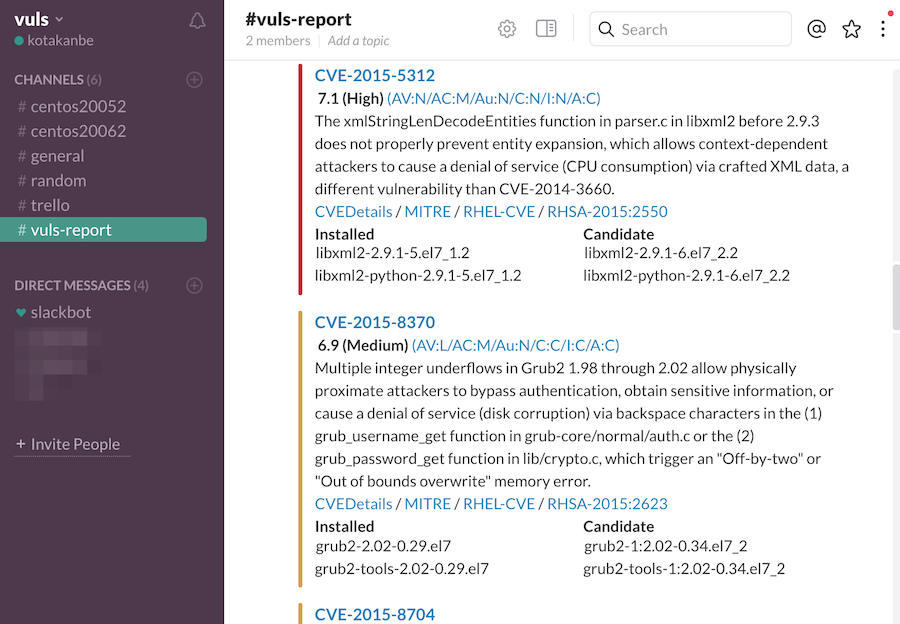
Vuls
Vulsis an advanced open-source vulnerability scanner designed specifically for Linux & FreeBSD systems.
It is an agentless scanner which means it doesnt require any software installation on the target machines.
It can be deployed on cloud platforms, on-premise systems, and also on Docker containers.
Vuls uses multiple vulnerability databases such as NVD, OVAL, FreeBSD-SA, and Changelog to perform high-quality scans.
The best thing is it can even detect vulnerabilities for which patches have not yet been published by distributors.
It supports both remote & local scan modes.
In remote scan mode you set up a central Vuls server that connects to the target servers via SSH.
Vuls can also detect vulnerabilities in non-operating system packages.
How to choose the best tool?
One thing that system administrators should remember is that each system is usually dependent on other programs.
For example, that is the case with ClamAV and OpenVAS.
you oughta understand what your system needs and in which areas it can be having vulnerabilities.
Firstly, use a lightweight tool to research what section needs attention.
Then use the proper tool to solve the problem.