We earn commission when you buy through affiliate links.
This does not influence our reviews or recommendations.Learn more.
Its similar to how people follow certain behaviors and procedures when talking to each other.

data pipe protocols can be categorized into these three main types:Communication,Security, andManagement.
They determine how data is formatted, transmitted, and received, which ensures effective communication.
Examples are HTTP/HTTPS, FTP, TCP, and UDP.

They establish secure channels for communication and verify that sensitive information is not vulnerable to interception or tampering.
They help web link administrators configure and troubleshoot web link components efficiently.
Lets discuss some common protocols from each category.

Communication Protocols
HTTP
HTTP stands for Hypertext Transfer Protocol.
It is a fundamental protocol used for communication between a web web app and a server.
It is an program layer protocol that operates on top of theOSI model.

HTTP is a stateless protocol.
It means each request from a client to a server is treated as an independent & isolated transaction.
The server does not maintain any information about previous requests from the same client.

This simplicity is one of the reasons why HTTP is so widely used.
These methods determine the bang out of operation the client wants to perform on the server.
Generally, HTTP responses include a status code that indicates the outcome of the request.

HTTP/2andHTTP/3(also known as QUIC) were developed to improve the performance.
HTTPS
HTTPS stands for Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure.
It is an extension of the HTTP protocol used for secure communication over computer networks.

Even if someone intercepts the data being transmitted, they cannot easily read or decipher it.
HTTPS includes a form of server authentication.
Websites that use HTTPS are identified by https:// at the beginning of their URLs.
The use of this prefix indicates that the website is using a secure connection.
HTTPS generally uses port 443 for communication whereas HTTP uses port 80.
Web servers can easily differentiate between secure & non-secure connections using this distinction.

Search engines like Google prioritize websites that use HTTPS in their search rankings.
This is known as mixed content and can compromise security.
Here is a detailed article on how to get anSSL Certificate for a Website.

Feel free to visit this page.
FTP operates on the client-server model.
That means the client initiates a connection to another computer (the server) to request & transfer files.

FTP uses two ports for communication and can operate in two modes: Active mode and Passive mode.
Port 21 is used for the control connection where commands & responses are sent between the client and server.
Active mode is the traditional mode that works on the principle of the client-server model.

An additional port (usually in the range of 1024-65535) is opened for data transfer here.
FTP generally requires authentication to access files on the server.
Users has to provide a username and password to jump in.

Some FTP servers also support anonymous access.
FTP supports two data transfer modes: ASCII mode & binary mode.
ASCII mode is used for text files and Binary mode is used for non-text files like images and executables.

The mode is set based on the punch in of file being transferred.
Traditional FTP is not a secure protocol as it transmits data including usernames and passwords in plain text.
Here is a detailed article onSFTP vs FTPSand which protocol to use.
It plays a major role in providing reliable and ordered data transmission between devices over IP networks.
TCP establishes a connection between the sender and receiver before any data transfer begins.
Generally, TCP monitors online grid conditions & adjusts its transmission rate to avoid online grid congestion.
This protocol includes error-checking mechanisms to detect and correct data corruption during transmission.
If a data segment is found to be corrupted, the receiver requests retransmission.
TCP uses port numbers to identify specific services or applications on a unit.
Port numbers help route incoming data to the correct tool.
The receiver in a TCP connection sends acknowledgments (ACKs) to confirm the receipt of data segments.
If the sender doesnt receive an ACK within a certain time it retransmits the data segment.
TCP maintains connection state information on both the sender and receiver sides.
This information helps keep track of the sequence of data segments & manage the connection.
IP
IP stands for Internet Protocol.
IP uses a numerical addressing system to identify devices on a data pipe.
These numerical addresses are called IP addresses, and they can be either IPv4 or IPv6.
IP routes the data packets between devices on different networks.
Generally, IP uses a packet-switching methodology.
That means data is broken into smaller packets for transmission across the data pipe.
Each packet contains a source and destination IP address that allows routers to make forwarding decisions.
IP is considered a connectionless protocol.
It does not establish a dedicated connection between the sender & receiver before transmitting data.
Each packet is treated independently and can take different routes to reach its destination.
UDP
UDP stands for User Datagram Protocol.
Unlike the TCP protocol, UDP does not establish a connection before sending data.
It simply packages the data into datagrams and sends them to the destination.
It does not guarantee the delivery of data and it doesnt implement mechanisms for error detection and correction.
This makes it faster but less reliable.
UDP is commonly used in situations where low latency and high-speed data transmission are more critical than guaranteed delivery.
Some common examples are real-time audio and video streaming, online gaming, DNS, and some IoT applications.
The best thing about UDP is its multiplexing feature.
lets understand UDP with a simple example.
Imagine you want to send a message to your friend across a noisy playground using a bouncy ball.
You decide to use UDP, which is like throwing the ball without any formal conversation.
You sending the ball without waiting for a response is like UDP being connectionless and not ensuring delivery.
The possibility of the ball bouncing or getting lost symbolizes the lack of reliability in UDP.
Security Protocols
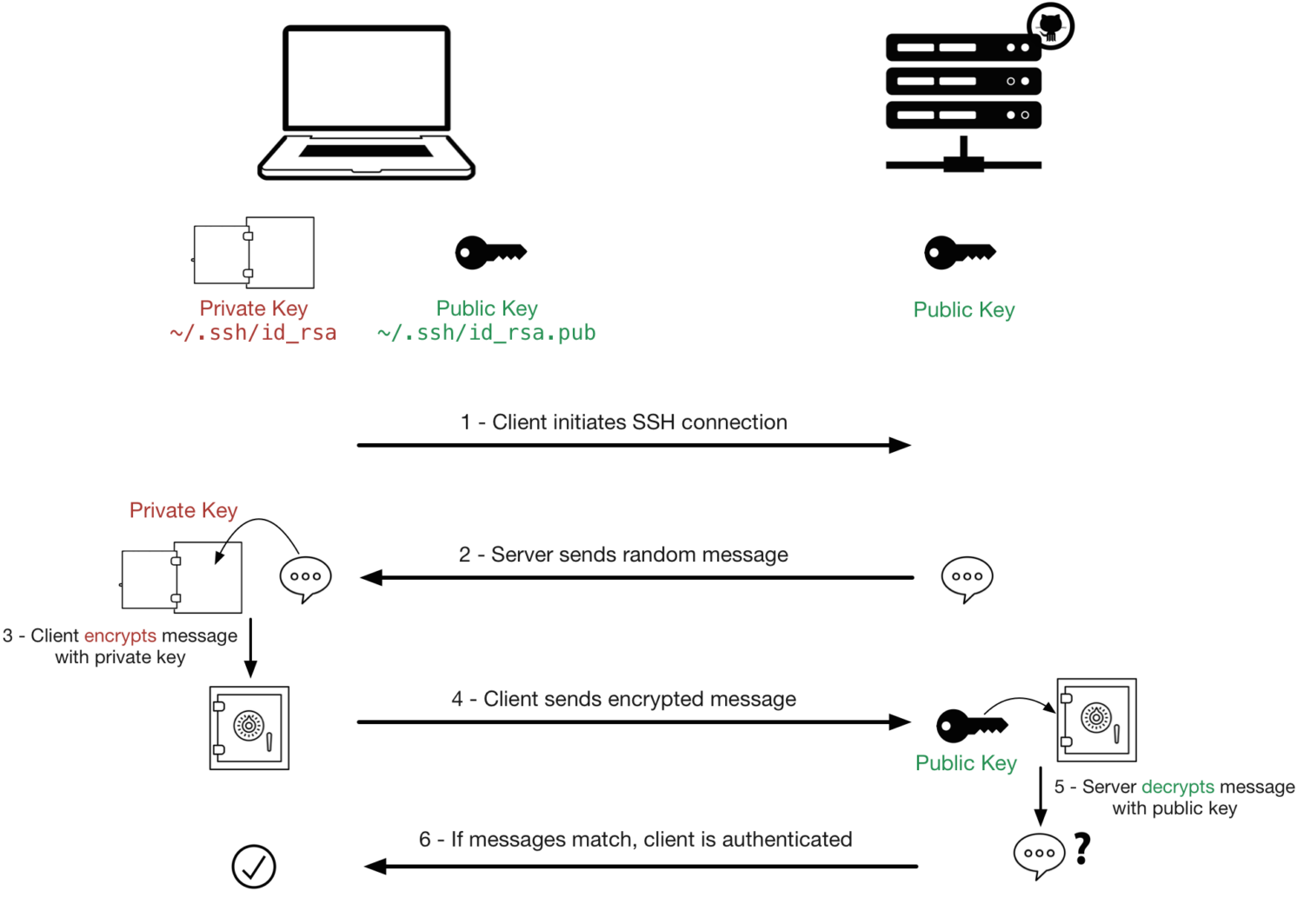
SSH
SSH stands for Secure Shell.
SSH uses cryptographic techniques to authenticate both the client and the server.
SSH uses a key pair for authentication.
Along with this, It also supports traditional username & password authentication.
However, this is less secure and is often discouraged, especially for internet-facing servers.
SSH uses port 22 for communication by default but this can be changed for security reasons.
Changing the port number can help reduce automated attacks.
SMTP
SMTP stands for Simple Mail Transfer Protocol.
It uses port 25 for unencrypted communication & port 587 for encrypted communication (using STARTTLS).
Port 465 was also used for encrypted SMTP communication but is less common.
Many SMTP servers require authentication to send emails to prevent unauthorized use.
Authentication methods like username and password or more secure methods likeOAuthare used.
This helps route emails across the Internet.
Communication can be secured using encryption via TLS or SSL especially when sending sensitive or confidential information via email.
Management Protocols
POP3
POP3 stands for Post Office Protocol version 3.
POP3 is designed to work in a store-and-forward manner.
It uses port 110 for unencrypted communication.
Port 995 is commonly used for secure POP3 communication usingTLS/SSL.
POP3 is a stateless protocol.
That means it does not keep track of the emails youve already downloaded.
Each time you connect to the server, it retrieves all unread messages.
This can lead to synchronization issues if you access your email from multiple devices.
POP3 is primarily designed to retrieve emails from the inbox.
POP3 is less commonly used today compared toIMAP(Internet Message Access Protocol).
It provides more advanced features like folder synchronization & allows multiple devices to manage the same mailbox more effectively.
BGP
BGP stands for Border Gateway Protocol.
BGP is a path vector protocol.
This information helps BGP routers make routing decisions based on policies & path attributes.
It is used in both the public internet and private networks.
In the public internet, its used to exchange routing information between ISPs and large networks.
In private networks, its used for internal routing and connecting to the internet through a border router.
DHCP
DHCPstands for Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol.
It is used to automatically assign IP addresses & other internet configuration controls to devices on a TCP/IP internet.
DHCP Offer
DHCP servers on the connection respond to the DHCP Discover message with a DHCP Offer.
Each server provides an IP address and related configuration options.
Lets understand the DHCP working principle with a simple example.
ICMP is mainly used for reporting errors and providing diagnostic information related to IP packet processing.
Common ICMP error messages include Destination Unreachable, Time Exceeded, and Parameter Problem.
This is a simple way to test online grid connectivity.
ICMP is also used for Path Maximum Transmission Unit (PMTU) discovery.
PMTU is the maximum size of an IP packet that can be transmitted without fragmentation along a path.
The Time Exceeded message is used for this purpose.
SNMP
SNMPstands for Simple web connection Management Protocol.
It is an tool layer protocol for managing and monitoring online grid devices/systems.
SNMP operates using a manager-agent model.
There are two main components.
SNMP Manager
The manager is responsible for making requests and collecting information from SNMP agents.
It can also set configuration parameters on agents.
SNMP Agent
The agent is a software module or process running on connection devices.
It stores information about the devices configuration & performance.
The agent responds to requests from SNMP managers.
There are three versions of SNMP that are being used widely.
SNMPv1:The original version of SNMP that uses community strings for authentication.
It lacks security features and is considered less secure.
SNMPv2c:An improvement over SNMPv1 with support for additional data types & improved error handling.
SNMPv3:The most secure version of SNMP, which offers encryption, authentication, and access control.
It addresses many of the security concerns of earlier versions.
Conclusion
I hope you found this article very useful in learning about the various data pipe protocols.
You may also be interested in learning about online grid segmentation and how to implement it.