We earn commission when you buy through affiliate links.
This does not influence our reviews or recommendations.Learn more.
A practical guide to hardening and secure Apache Tomcat Server with the best practices.
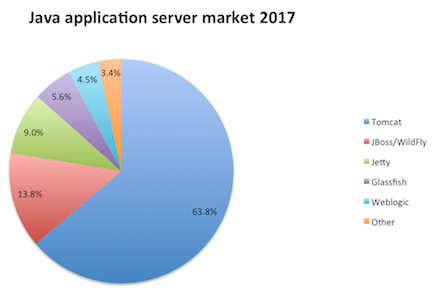
Tomcat is one of the most popular Servlet and JSP Container servers.
Technically, you might use Tomcat as a front-end server to serve site requests directly.
Using a web server to handle the requests givesperformanceandsecuritybenefits.
If you are using Apache HTTP as a front-end web server, then you must considersecuring that as well.
Good knowledge of Tomcat &UNIX commandis mandatory.
Notes
We require some tool to examine HTTP Headers for verification.
There are two ways you’re free to do this.
If testingInternet-facingapplication, then you may use the following HTTP Header tools to verify the implementation.
And for anIntranet system, you may use Google Chrome, Firefox developer tools.
As a best practice, you must take abackupof any file you are about to modify.
We will call Tomcat Installation folder as$tomcatthroughout this guidelines.
Lets go through the hardening & securing procedures.
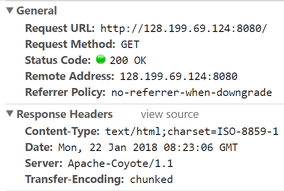
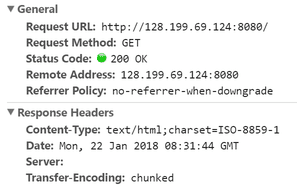
Having a server banner expose the product and version you are using and leads to information leakage vulnerability.
By default, a page served by Tomcat will show like this.
Lets hide the product and version details from the Server header.
Running Tomcat with a security manager is better than running without one.
Tomcat has excellent documentation onTomcat Security Manager.
The good thing about this is you dont need to change any configuration file.
Its just the way you executestartup.shfile.
All you got to do is to start tomcat withsecurityargument.
Enable SSL/TLS
Serving web requests over HTTPS is essential to protect data between client and Tomcat.
to make it make your web utility accessible through HTTPS, you gotta implement SSL certificate.
Change the Keystore file name and password with yours.
If you need help with the keystore & CSR process, then refer tothis guide.
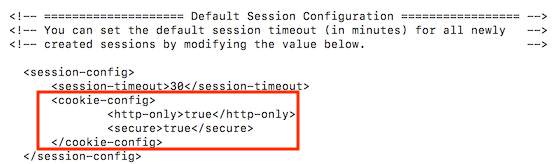
Enforce HTTPS
This is only applicable when youve SSL enabled.
If not, it will break the app.
Its a flag which is injected in the response header.
Run Tomcat from non-privileged Account
Its good to use a separate non-privileged user for Tomcat.
The idea here is to protect other services running in case of any of account get compromised.
you might delete them to keep it clean and avoid any known security risk with Tomcat default utility.
You see, having default configuration leads to high-security risk.
Its recommended to change tomcat shutdown port and default command to something unpredictable.
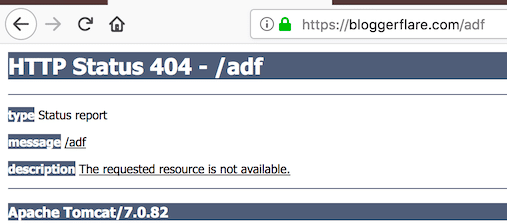
Lets look at the default 404 page.
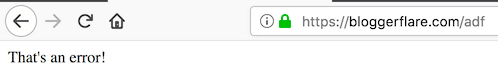
you’re free to do this forjava.lang.Exceptionas well.
This will help in not exposing tomcat version information if any java lang exception.
Just add following inweb.xmland restart tomcat server.
I hope the above guide gives you an idea of securing Tomcat.
If you are looking to learn more about Tomcat administration, then check out thisonline course.