We earn commission when you buy through affiliate links.
This does not influence our reviews or recommendations.Learn more.
A practical guide to secure and harden Apache HTTP Server.

The Web Server is a crucial part of web-based applications.
Having default configuration supply much sensitive information which may help hacker to prepare for an attack of the applications.
Interesting research byPositive Technologiesreveals, 52% of the scanned applications had high vulnerabilities.

Fair knowledge of Apache Web Server & UNIX command is mandatory.
Notes
You require some tool to examine HTTP Headers for some of the implementation verification.
There are two ways to do this.

Exposing version means you are helping hacker to speedy the reconnaissance process.
The default configuration will expose Apache Version and OS throw in as shown below.
ServerSignaturewill remove the version information from the page generated by Apache.

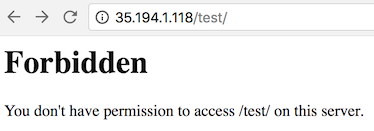
Lets test how does it look like in default configs.
As you could see, it displays a forbidden error instead of showing test folder listing.
To prevent this vulnerability, lets implement it as below.
This is required to fix for PCI compliance.
Run Apache from a non-privileged account
A default installation runs as nobody or daemon.
Using a separate non-privileged user for Apache is good.

The idea here is to protect other services running in case of any security hole.
Thats because Apache is listening on port 80 and it has to be started with root.
it’s possible for you to disallow another user to get into conf and bin folder.

System options Protection
In a default installation, users can override apache configuration using .htaccess.
This must be done at the root level.
Disable Trace HTTP Request
By default Trace method is enabled in Apache web server.
Lets see how it looks like in default configuration.
As you could see in above TRACE request, it has responded my query.
Lets disable it and test it.
Now, this web server doesnt allow TRACE request and help in blocking Cross Site Tracing attack.
Clickjacking Attack
Clickjacking is a well-known web utility vulnerabilities.
X-Frame-Options supports two more options, which I explainedhere.
SSI attack allows the exploitation of a web app by injecting scripts in HTML pages or executing codes remotely.
X-XSS Protection
Cross Site Scripting (XSS) protection can be bypassed in many browsers.
You could apply this protection for a web tool if it was disabled by the user.
This is used by a majority of giant web companies like Facebook, Twitter, Google, etc.
As you’re able to see, XSS-Protection is the injected in the response header.
Disable HTTP 1.0 Protocol
When we talk about security, we should protect as much we can.
So why do we use older HTTP version of the protocol, lets disable them as well?
HTTP 1.0 has security weakness related to session hijacking.
We can disable this by using the mod_rewrite module.
To mitigate this, you’re able to lower the timeout value to maybe 60 seconds.
SSL
Having SSL is an additional layer of security you are adding into Web system.
However, default SSL configuration leads to certain vulnerabilities, and you should consider tweaking those configurations.
SSL Key
Breaching SSL key is hard, but not impossible.
Its just a matter of computational power and time.
So the higher key length you have, the more complicated it becomes to break SSL key.
The majority of giant Web Companies use 2048 bit key, as below so why dont we?
you could use OpenSSL to generate CSR with 2048 bit as below.
It will generate a CSR which you will need to send to acertificate authorityto sign it.
Data encryption is the process of converting plain text into secret ciphered codes.
Its based on your web server SSL Cipher configuration the data encryption will take place.
So its important to configure SSL Cipher, which is stronger and not vulnerable.
Any SSL v2/v3 communication may be vulnerable to a Man-in-The-Middle attack that could allow data tampering or disclosure.
Lets implement apache web server to accept only latest TLS and reject SSL v2/v3 connection request.
Mod Security
Mod Security is anopen-source web app firewall, which you could use with Apache.
It comes as a module which you have to compile and install.
If you cant afford acommercial web system firewall, this would be an excellent choice to go for it.
The mod_unique_id module is pre-requisite for Mod Security.
Mod Security is now installed!
You have successfully configured Mod Security with Apache!
Now, Apache Web server is protected by Mod Security web utility firewall.
In this section, we will do all configuration modification in /opt/apache/conf/crs/modsecurity_crs_10_setup.conf.
We will refer /opt/apache/conf/crs/modsecurity_crs_10_setup.conf as setup.conf in this section for example purpose.
Its important to understand what are the OWASP rules are provided for free.
There are two types of rules provided by OWASP.
Base Rules these rules are heavily tested, and probably false alarm ratio is less.
Experimental Rules these rules are for an experimental purpose, and you may have a high false alarm.
Its important to configure, test and implement in UAT before using these in a production environment.
Optional Rules these optional rules may not be suitable for the entire environment.
Based on your requirement you may use them.
If you are looking for CSRF, User tracking, Session hijacking, etc.
protection, then you may consider using optional rules.
These rules configuration file is available in crs/base_rules, crs/optional_rules and crs/experimental_rules folder.
Lets get familiar with some of the base rules.
There are two types of logging available; Debug & Audit log.
Debug Log: this is to duplicate the Apache error, warning and notice messages from the error log.
By default configuration will write both logs.
However, you’ve got the option to change based on your requirement.
The log is controlled inSecDefaultActiondirective.
Lets write audit log into /opt/apache/logs/modsec_audit.log by adding as shown below.
Rule Engine enabling or disabling is controlled bySecRuleEnginedirective.
as we have installed Core Rule and turned on Rule Engine.
Lets test a few of them.
Ex /etc/passwd, .htaccess, etc.
Lets go one step ahead, how about keeping server name whatever you wish?
Its possible withSecServerSignaturedirective in Mod Security.
You see its interesting.
Ex:
General Configuration
Lets check out some of the general configurations as best practice.
This is quite common in the shared environment.
Access Logging
Its essential to configure access log properly in your web server.
By default, Apache is not configured to capture these data.
You got to configure them manually as follows.
you might referhttp://httpd.apache.org/docs/2.2/mod/mod_log_config.htmlfor a complete list of parameter supported in LogFormat directive in Apache Web Server.
Info Module The mod_info module can leak sensitive information using .htaccess once this module is loaded.
If you are new to Apache HTTP, then I would recommend takingthe Apache HTTP administration course.
These steps reduce vulnerabilities and strengthen your web server against threats.