We earn commission when you buy through affiliate links.
This does not influence our reviews or recommendations.Learn more.
In this article, you will learn about different ways to play around with commits in Git.
So lets get started and understand what git reset, revert and rebase are.
Git Reset
Git reset is a complex command, and it is used to undo the changes.
you’re free to think of git reset as a rollback feature.

With git reset, you might jump between various commits.
There are three modes of running a git reset command: soft, mixed, and hard.
By default, git reset command uses the mixed mode.

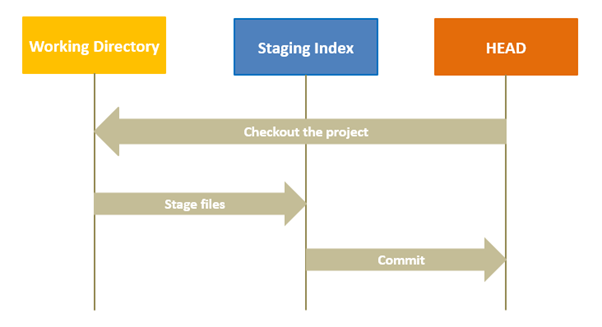
Staging Area (Index) is where git tracks and saves all the changes in the files.
The saved changes are reflected in the .git directory.
You use git add filename to add the file to the staging area.

The current branch in Git is referred to as HEAD.
It points to the last commit, which happened in the current checkout branch.
It is treated as a pointer for any reference.
Once you checkout to another branch, the HEAD also moves to the new branch.
Let me explain how git reset works in hard, soft, and mixed modes.
In soft reset, only the pointer is changed to the specified commit.

The files of all the commits remain in the working directory and staging area before the reset.
In mixed mode (default), the pointer and the staging area both get reset.
It will remove all the commits with happened after the specified commit.

This command will change the commit history and point to the specified commit.
In this example, I will add three new files, commit them and then perform a hard reset.
Now, I will create 3 files and add some content to it.
Add these files to the existing repository.
When you rerun the status command, it will reflect the new files I just created.
Before committing, let me show you, I currently have a log of 3 commits in Git.
Now, I will commit to the repository.
If I do ls-files, you will see the new files have been added.
Now, I will spin up the hard reset command.
If I check the log of git, this is how it will look.
Let me show you one more example.
you might see the head pointer has now changed to 0db602e from d69950b.
Git Soft Reset
Similarly, now I will show you an example of a soft reset.
Consider, I have added the 3 files again as mentioned above and committed them.
The git log will appear as shown below.
Details of the commit in the log can be seen using the below command.
you better pass more than 6 starting characters of SHA, the complete SHA is not required.
They have not got deleted.
Thats why you should use a soft reset rather than a hard reset.
There is no risk of losing the files in the soft mode.
In short, it is fair to say that the git revert command is a commit.
The Git revert command does not delete any data while performing the revert operation.
Lets say I am adding 3 files and performing a git commit operation for the revert example.
The log will show the new commit.
Now I would like to revert to one of my past commits, lets say 59c86c9 new commit.
I would spin up the command below.
After you save and kill the file, this is the output you will get.
Now to make the necessary changes, unlike reset, revert has performed one more new commit.
If you check the log again, you will find a new commit because of the revert operation.
Git log will have all the history of commits.
As a developer, I would not create my features on the master branch in a real-world scenario.
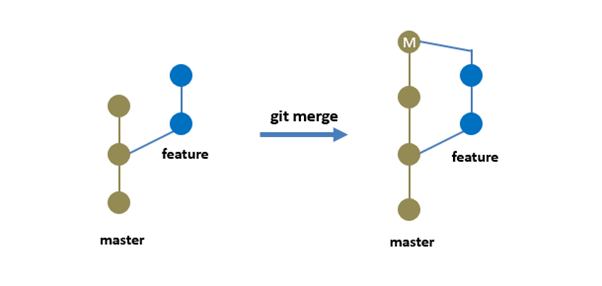
Rebase can sometimes be a little confusing to understand because it is very similar to a merge.
It becomes confusing to trace.
So, this is where rebase is going to help.
So, behind the scenes, git is duplicating the feature branch commits on the master branch.
This approach will give you a clean straight-line graph with all the commits in a row.
It makes it easy to trace what commits went where.
Let me show you this practically.
This is how my master branch looks like currently.
It has 4 commits.
I will create feature 1 and commit it to the feature branch.
I will create one more feature, i.e., feature 2, in the feature branch and commit it.
Now I want to add these two new features to the master branch.
For that, I will use the rebase command.
From the feature branch, I will rebase against the master branch.
What this will do is it will re-anchor my feature branch against the latest changes.
Now I am going to go ahead and checkout the master branch.
And finally, rebase the master branch against my feature branch.
That was all about reset, revert and rebase commands in Git.
Conclusion
That was all about reset, revert and rebase commands inGit.
I hope this step-by-step guide was helpful.