We earn commission when you buy through affiliate links.
This does not influence our reviews or recommendations.Learn more.
It is very useful in the hands of a Linux power user.

However, using it without regex can limit its capabilities.
But what is Regex?
Regex is regular expressions which you’ve got the option to use to improve grep search functionality.
Regex, by definition, is an advanced output-filtering pattern.
In our tutorial, well learn how to use Grep and Regex effectively.
Pre-Requisite
Using grep with regex requires good Linux knowledge.

You also need access to a laptop or computer running the Linux operating system.
you might use anyLinux distroof your choice.
Check out our detailed take on it here.
Access to the command line/terminal allows you to run all the commands provided in our grep/regex tutorial.
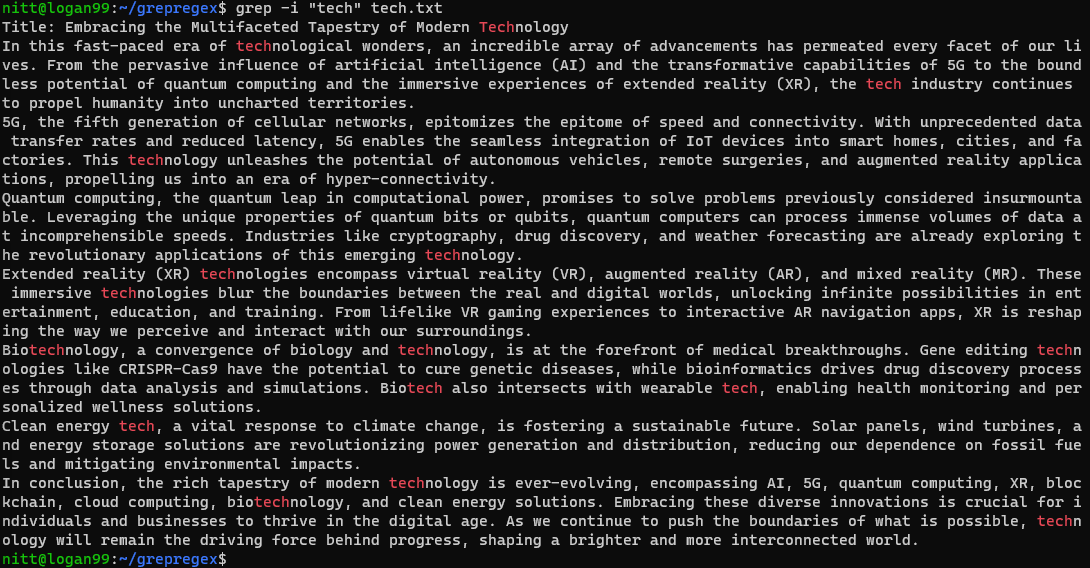
I used ChatGPT to generate a wall of text, telling it to write about tech.
The prompt that I used is as below.

Generate 400 words on tech.
It should include most tech.
Also, ensure that you repeat technology names across the text.
Lastly, a basic understanding of the grep command is a must.
you might check out16 grep command examplesto refresh your knowledge.
Well also introduce the grep command briefly to get you started.

Syntax and Examples of grep Command
Thegrepcommand syntax is simple.
Therere plenty of grep options available that modify its functionality.
By using it, you bypass any strings that match the given pattern.

It then marks them with red color.
Here, the | pipe symbol is escaped so that grep doesnt process it as a metacharacter.
#2.Case-Insensitive Search
To do a case-insensitive search, use grep with the-iargument.
The output shows all the lines that dont contain the word tech.
Also youll see empty lines as well.
These lines are the lines that are after a paragraph.

#4.Do a Recursive Search
To do a recursive search, use the-rargument with grep.
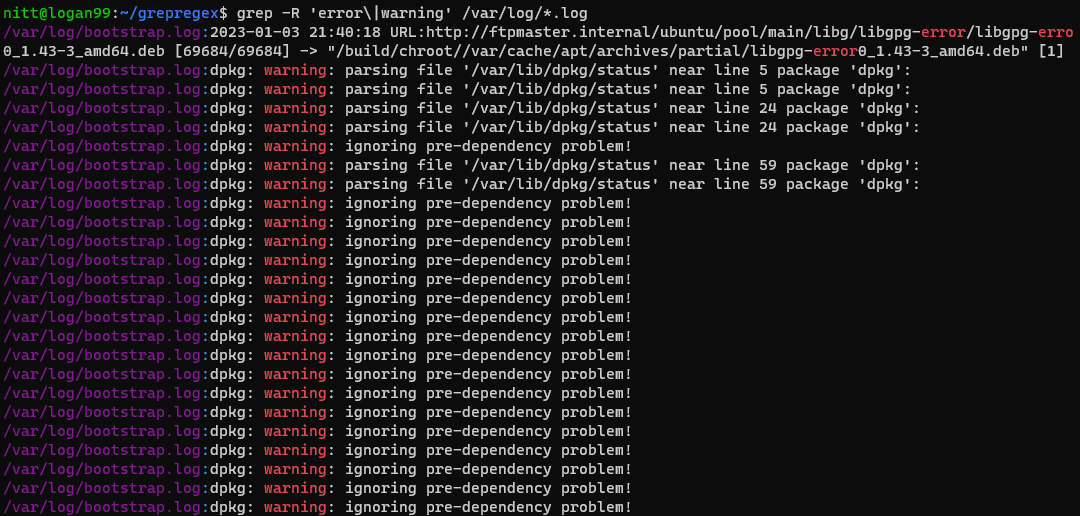
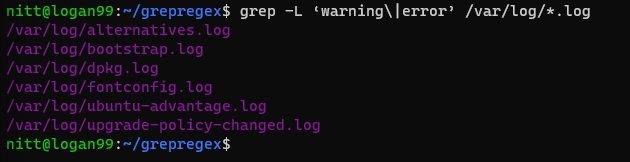
The grep command recursively searches for two words, error and warning, in the /var/log directory.
This is a handy command to learn about any warnings and errors in the log files.
These include:
The grep command uses BRE as the default option.
So, if you want to use other regex modes, youll need to mention them.
The grep command also treats metacharacters as they are.

The syntax of grep with regex is as below.
Lets see grep and regex in action with the examples below.
After all, a word is also a regex.

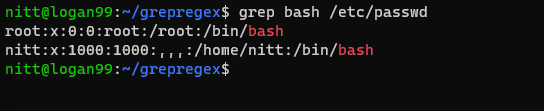
Similarly, it’s possible for you to also use literal matches to find current users.
To do so, run,
This displays the users that can reach the bash.
#2.Anchor Matching
Anchor matching is a useful technique for advanced searches using special characters.

In regex, there are different anchor characters that you might use to represent specific positions within a text.
Lets go through examples to get a clear idea.
Using caret requires entering the word or pattern in the correct case.
Thats because it is case-sensitive.
So, if you spin up the following command, itll not return anything.
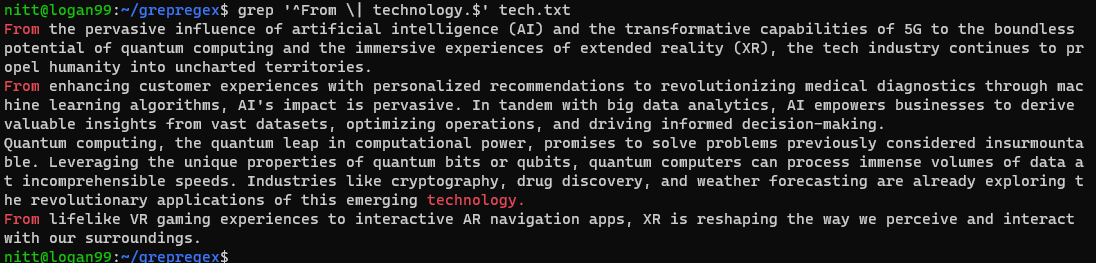
you’ve got the option to combine both ^ and $ symbols as well.
Lets look at the example below.
As you could see, the output contains sentences starting with From and sentences ending with technology.
#3.Grouping
If youre looking to search multiple patterns at once, youll need to use Grouping.
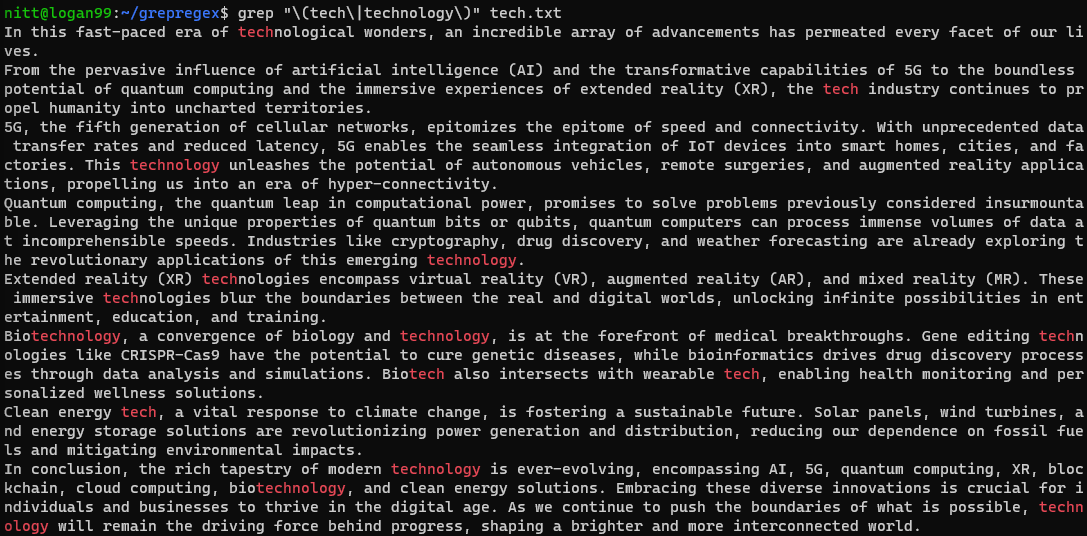
It helps you create small groups of characters and patterns that you could treat as a single unit.
With grouping, you’re able to match repeated patterns, capture groups, and search for alternatives.
Lets see an example of an alternative search.

Lets see it in the example below.
And what about capturing and non-capturing groups?
And, for non-capturing groups, youll need to use the ?

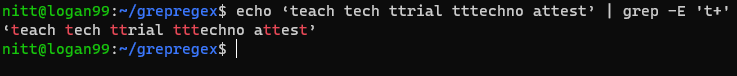
Lastly, we have repeated patterns.
Youll need to modify the regex to check for repeated patterns.
Here, the regex looks for one or more instances of the t character.

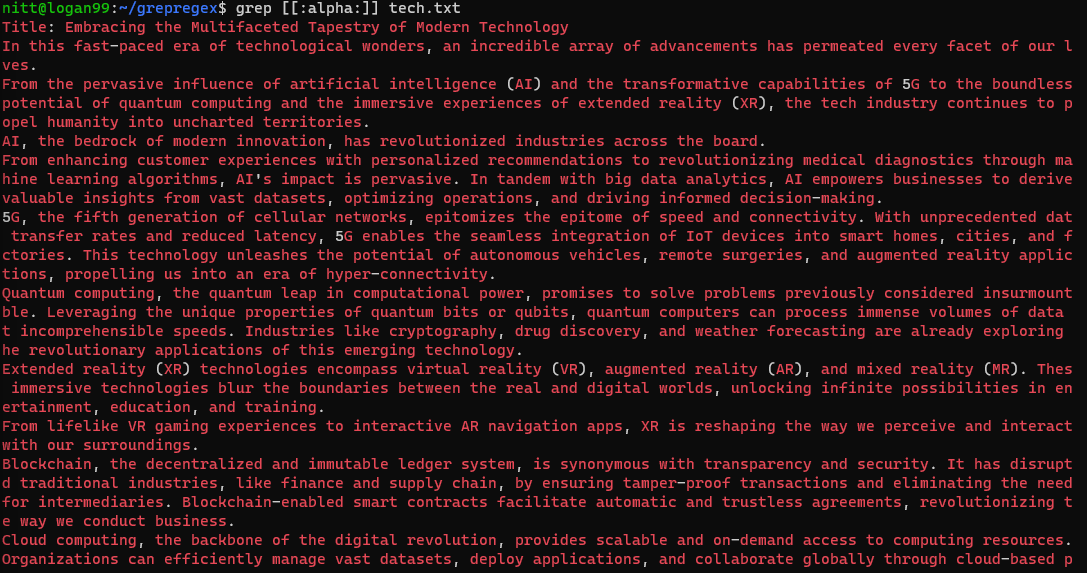
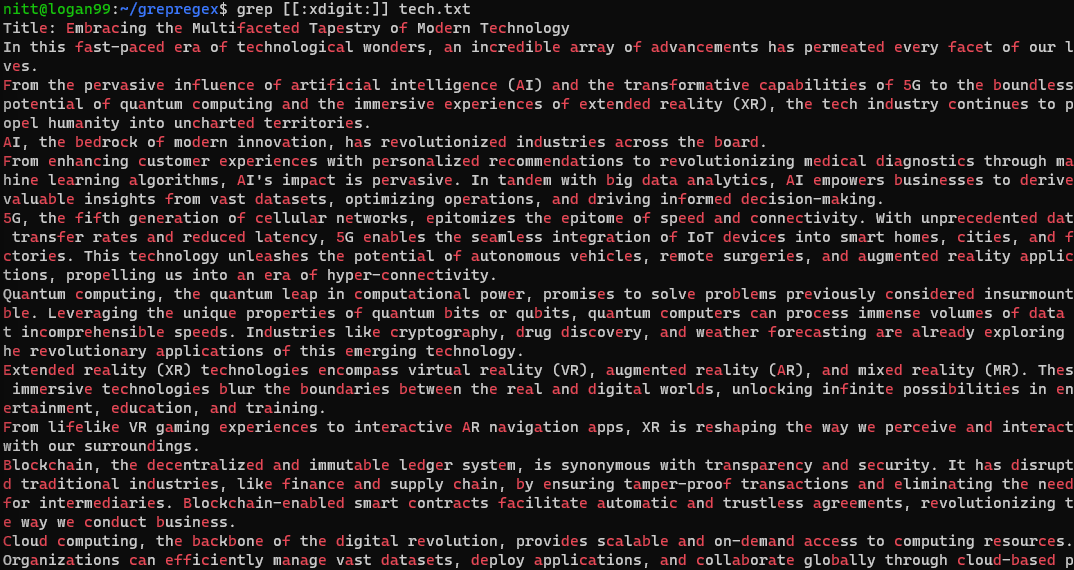
#4.Character Classes
With character classes, you’re able to write regex expressions easily.
These character classes use square brackets.
Some of the well-known character classes include:
And so on!
Lets check a few of them in action.
#5.Quantifiers
Quantifiers are metacharacters and are at the core of regex.
These let you match exact appearances.
Lets look at them below.
Here, it searches for the tcharacter instances for one or more matches.
Here-Estands for extended regex (that well discuss later.)
It removes the need to add escape characters.
To do so, youll need to use the -E flag.
For example, you could write \d which denotes [0-9].
For example, you might use PCRE to search for email addresses.
Here, PCRE ensures that the pattern is matched.
Similarly, you might also use a PCRE pattern to check for date patterns.
The command finds the date inYYYY-MM-DDformat.
you might modify it to match other date format as well.
The output lists the file names containing warning or error.
Final Words
This leads us to the end of our grep and regex guide.
you could use grep with regex extensively to refine searches.
Next, check out frequently asked Linux interview questions and answers.