We earn commission when you buy through affiliate links.
This does not influence our reviews or recommendations.Learn more.
Repetition of the same task is boring and painful for programmers like us.
One of such tasks is interactive with GitHubs private repository.
You know what it is.
And you are searching for ways to resolve it and landed on this article.
You will stop searching after reading this article.
So, here we are going to talk about accessing GitHub private repository without a password.
Without further ado, lets get started.
There are two ways to access any GitHub repository.
Most of you are usingHTTPS.
There is no problem when it comes to accessing the public repositories.

But, we need to authenticate ourselves whileaccessing a private repository.
There are different ways to authenticate ourselves.
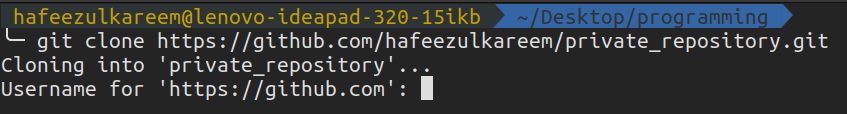
Lets quickly see how to access a private repository using it.

Thats it; we have cloned the private repository using theHTTPSmethod.
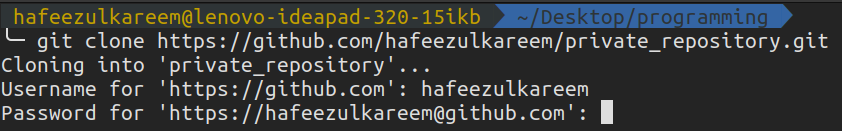
Now, update something in the repository, commit and push them to remote.
What did you notice?
Its again asking for the authentication.
Isnt it a boring and heavy task to enter credentials every time we interact with the private repository?
Yeah, it is.

We cant enter our GitHub credentials whenever we interact with our private repository.
Its a time-taking process and slows down our work.
There are different ways to get rid of the above problem.

The best way to do it is to useSSH.
But, there are other ways to do it.
Lets look at all of them one by one.

.git config
All the information about our repositories versions is stored in.gitdirectory.
Its a hidden folder.
There is aconfigfile in it that allows us to configure the prefs.
But, its not recommended in general.
We can clone a private repository by adding ourusernameandpasswordin the repository URL as follows.
Update theusername,password, andrepository_namewith appropriate details.
So, we are going to follow the above method of authentication and update our repository configuration accordingly.
Lets see the steps to get rid of repetitive authentication by updating the URL.
Now, again update something in the repository, commit and push them.
Do you observe anything?
It shouldnt have asked for your GitHub credentials this time.
So, we have solved our problem by updating our repository setting.
You might have noticed that its not secure.
As we are exposing our credentials.
And this method wont work in case your GitHub password contains@character.
So, there are some critical disadvantages of using this method.
Hence lets ignore it and move to the next method.
credential.helper
Thecredential.helperallows us to store the credentials forever in~/.git-credentialsfile.
It will store our credentials when we enter them for the first time.
So, thats one of the ways to avoid our problem.
Lets see it in action with precise steps.
Now, again the same process to check whether its working correctly or not.
Update, commit and push.
Going fine…
What if you want to save the credentials for4hours instead of forever?

Thecredential.helperprovides a way to store our credentials temporarily for a certain amount of time.
We usecacheinstead ofstoreto store the credentials for a certain amount of time.
Thecachewill store our credentials for15 minutesby default.
After 15 minutes, the git will again ask for credentials.
But, we can change the default time using the following command.
Dont forget to give the time in seconds.

Lets see it in action.
Now, update, commit and push.
Again it wont ask for your credentials as we have said it to cache them.
We have shown you the commands to work a git initialized repository.
We can update thegitconfiguration globally for all projects by adding the–globalflag in the above commands.
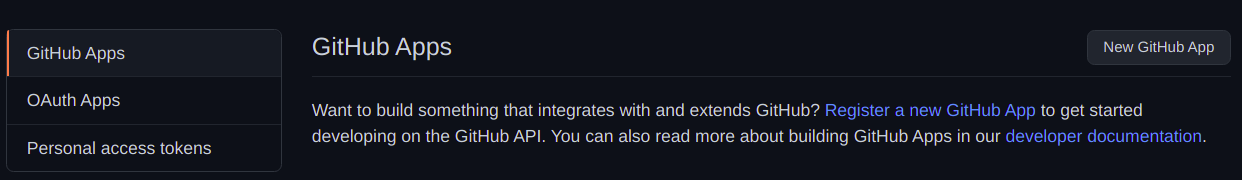
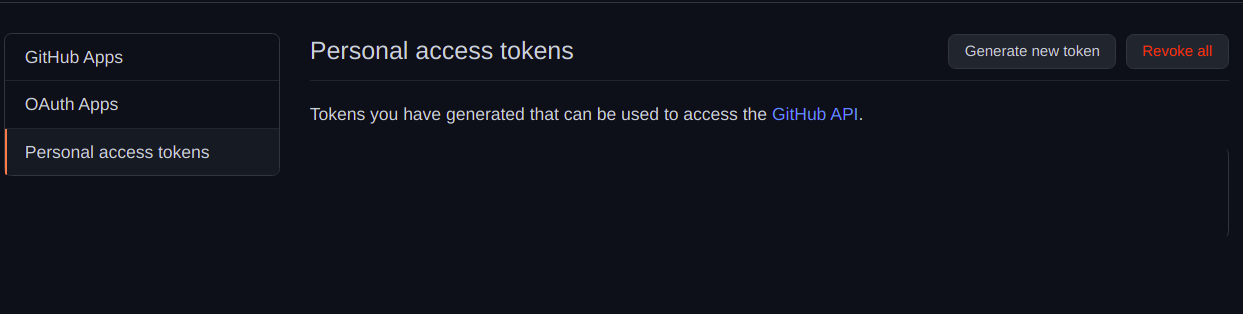
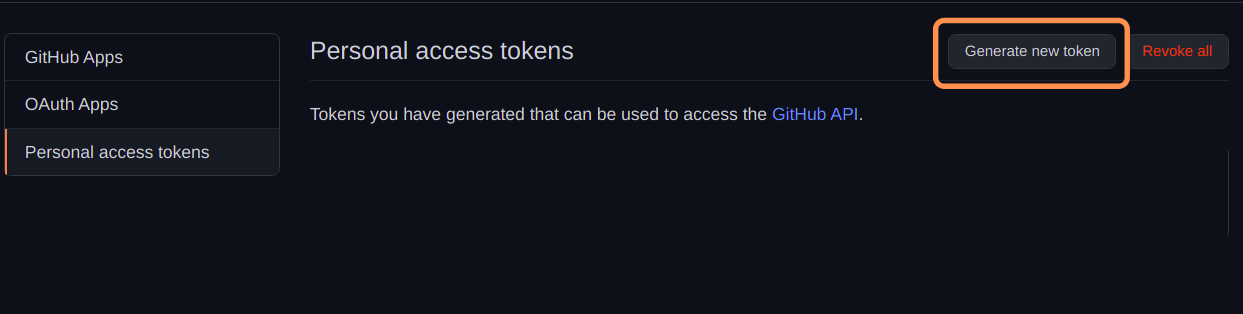
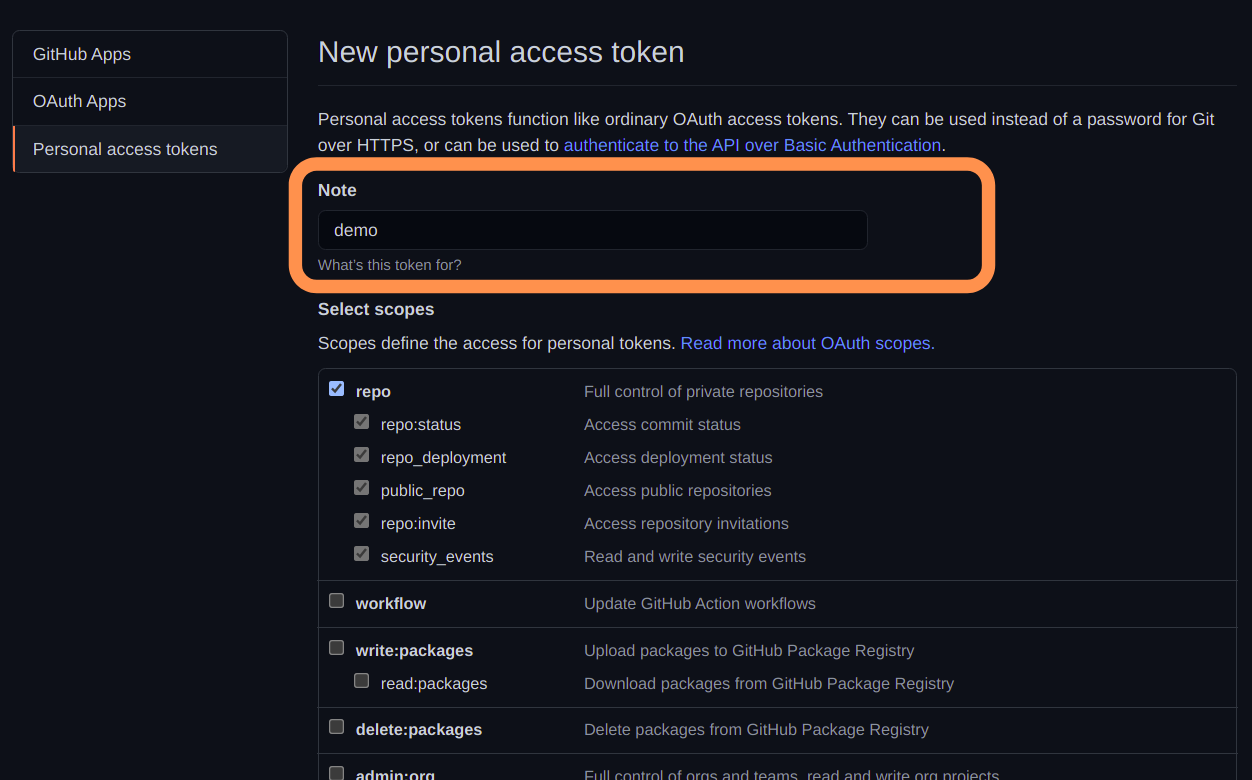
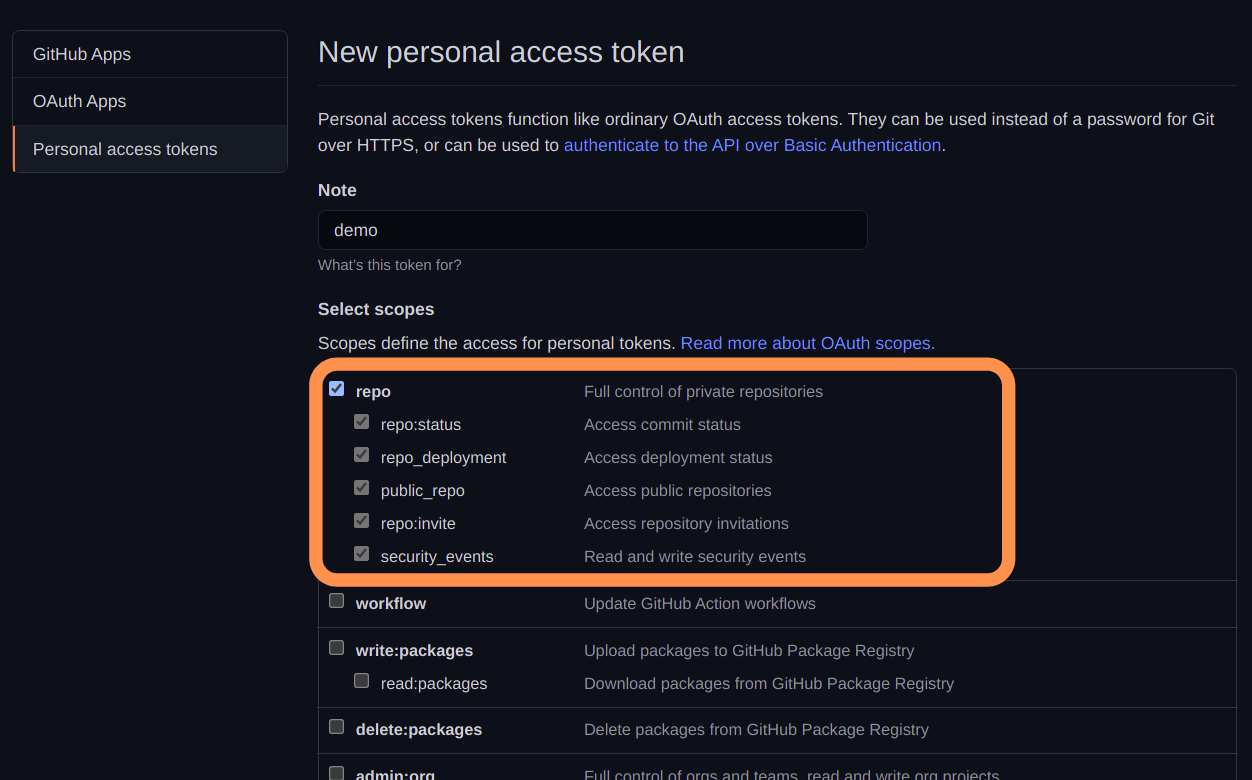
Personal Access Tokens
The personal access tokens are used to give access to the GitHub API.
The personal access tokens are likeOAuthtokens.
So, they can be used for basic authentication instead of a password forgit.
Hence, we can use the personal access tokens to resolve our problem.
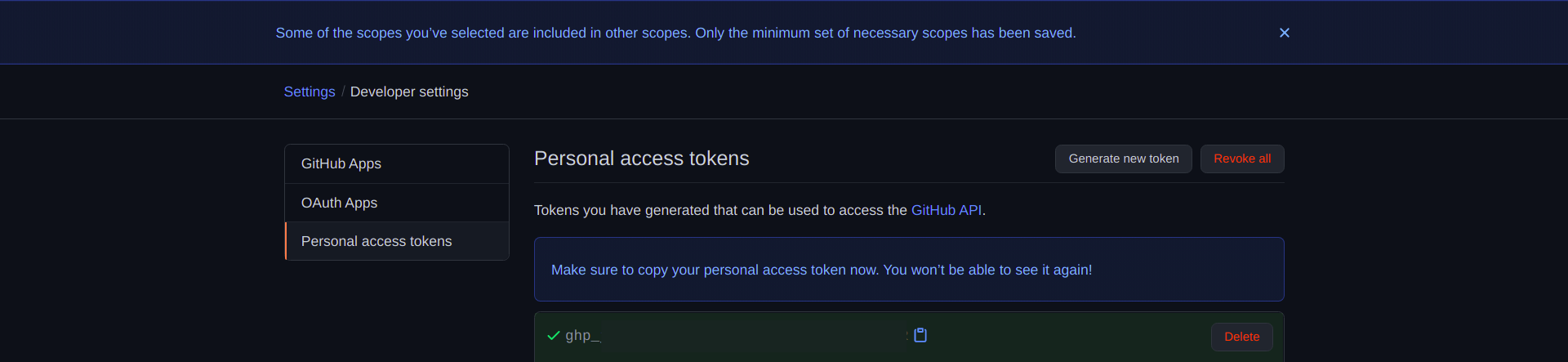
Lets see how to do it.
Now, make a run at reach the private repository.
Did it ask you for the authentication?
No, it wont ask you for the authentication until the token is active.
Lets move to the last way to resolve our problem.
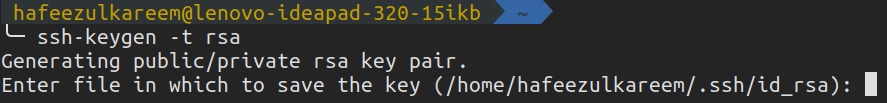
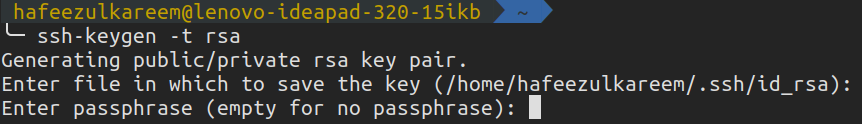
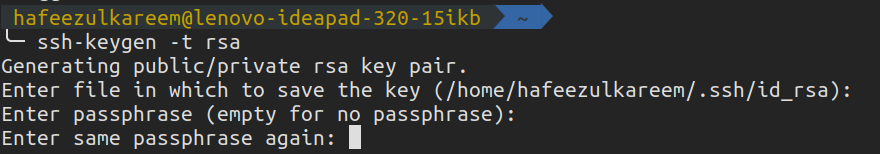
SSH
SSH is used to authenticate ourselves.
You find the full document about SSH in GitHubhere.
The idea is simple.
Generate an SSH key, add it to the GitHub account and enjoypasswordless authentication.
Lets see these three steps in detail.
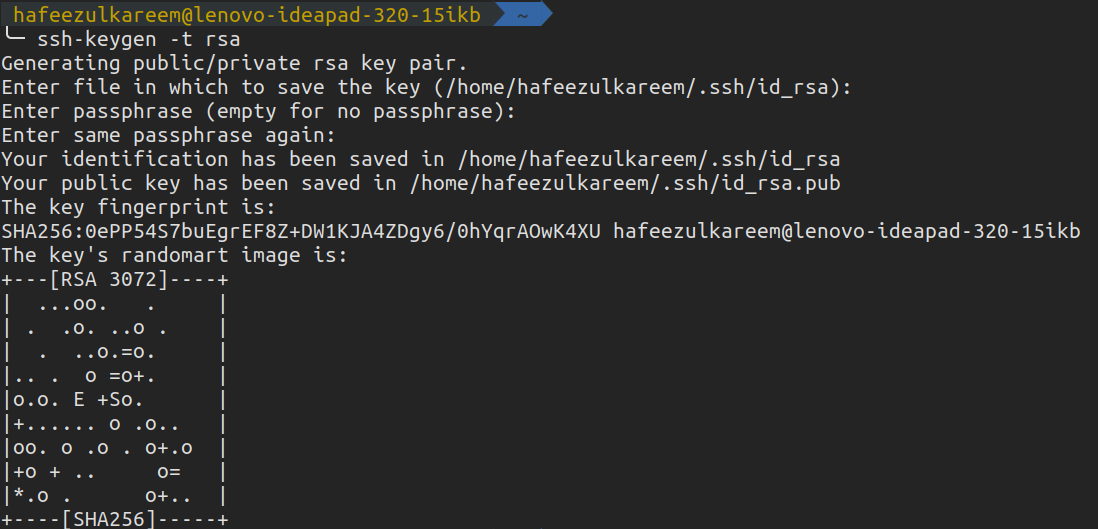
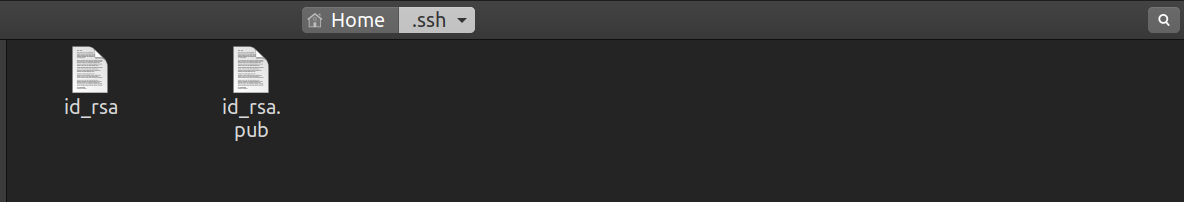
We have successfully generated a new SSH key in our systems.
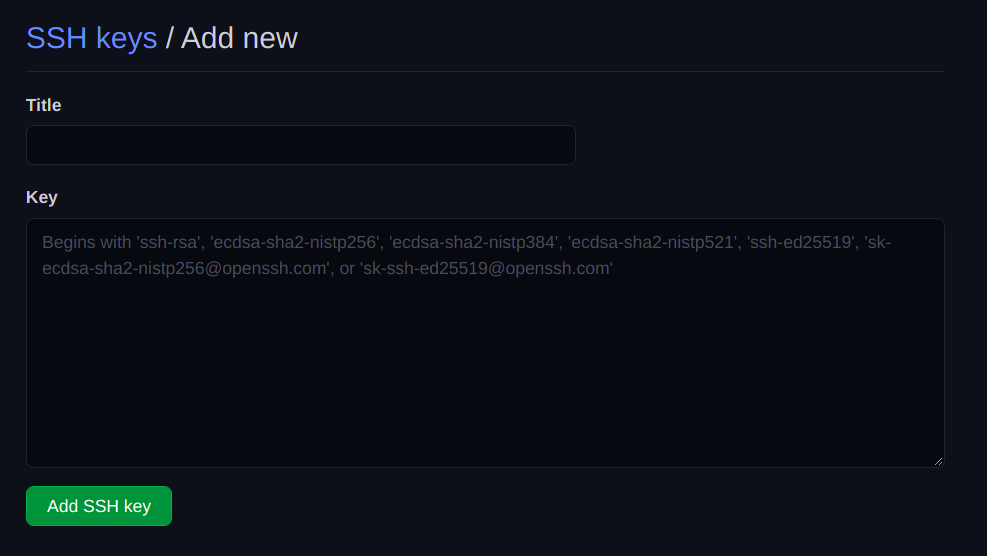
Now, its time to connect with our GitHub account.
The contents in the file with the extension.pubneed to be copied to our GitHub account for the connection.
In my case, itsid_rsa.pub.
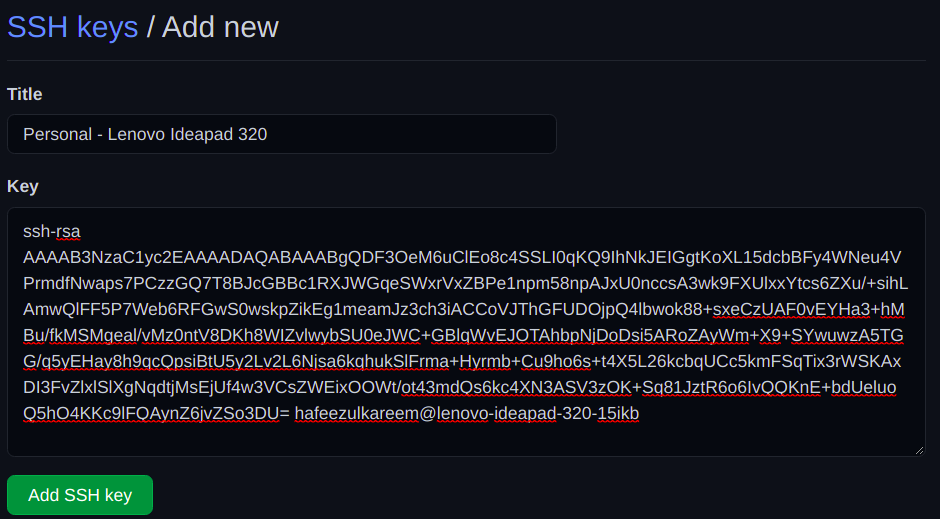
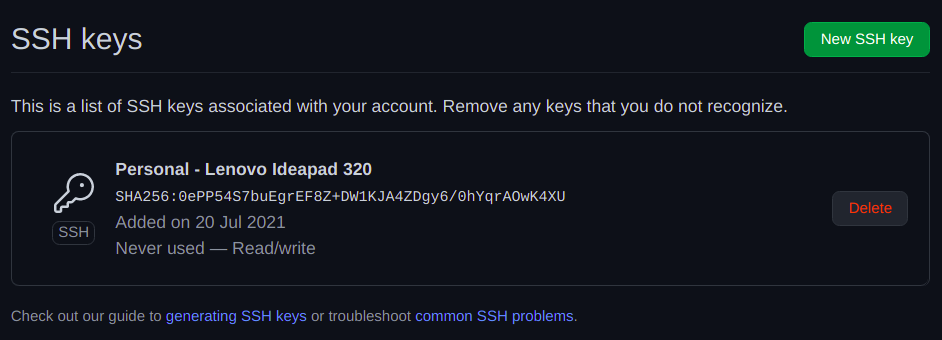
We have added our newly generated SSH key to GitHub.
Now, we have to authenticate the SSH connection to enjoy passwordless authentication later.
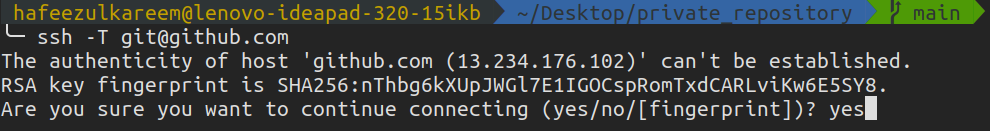
To do it, enter the following command in terminal or cmd.
It will ask for confirmation.
And thats it, and we are done.
Now, clone your private repository.
It wont ask for any authentication this time.
Update, commit and push.
It wont ask you for the authentication anymore.
Conclusion
Phew!
we have covered various methods to access private repositories without entering credentials all the time.
You may use any method.
But, the general and best practice is to use theSSHmethod for authentication.
Again its up to your preference; theres no strict rule to use the onlySSHmethod.
But, most businesses use theSSHmethod for authentication, which is secure and saves a lot of time.
And confirm yourcredentialsare safe.