We earn commission when you buy through affiliate links.
This does not influence our reviews or recommendations.Learn more.
However, ensuring optimal performance in these integrated systems can be a complex task.

If the level of effort required for improvement becomes too high, it is no longer considered optimization.
In such cases, it is referred to as system refactoring.
it’s possible for you to achieve some parts of this target even without changing the source code.
For example, through strategies such as rightsizing instances or leveraging spot instances for non-critical workloads.
AWS even defines cost optimization as one of the performance efficiency pillars of a well-architected framework.
All such actions will delay or even completely remove the necessity of system refactoring in the long run.
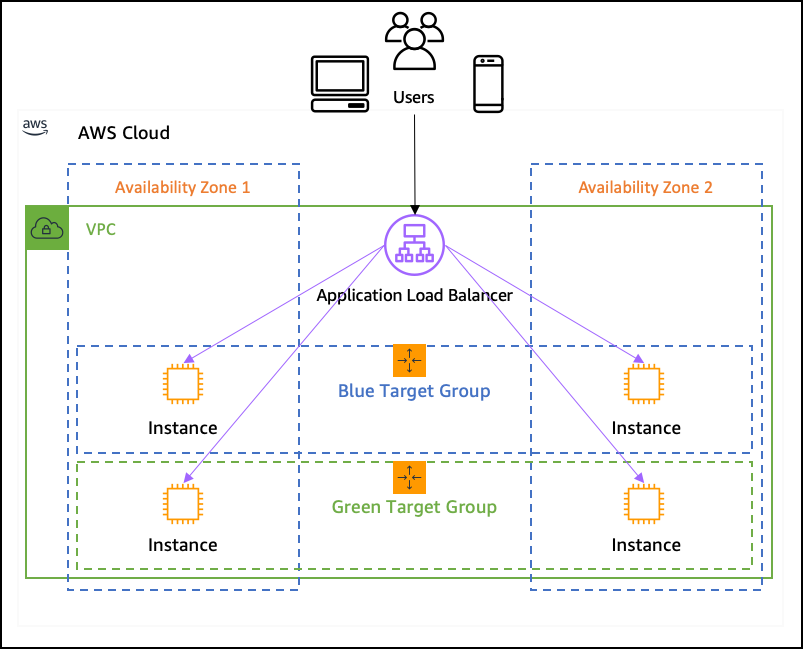
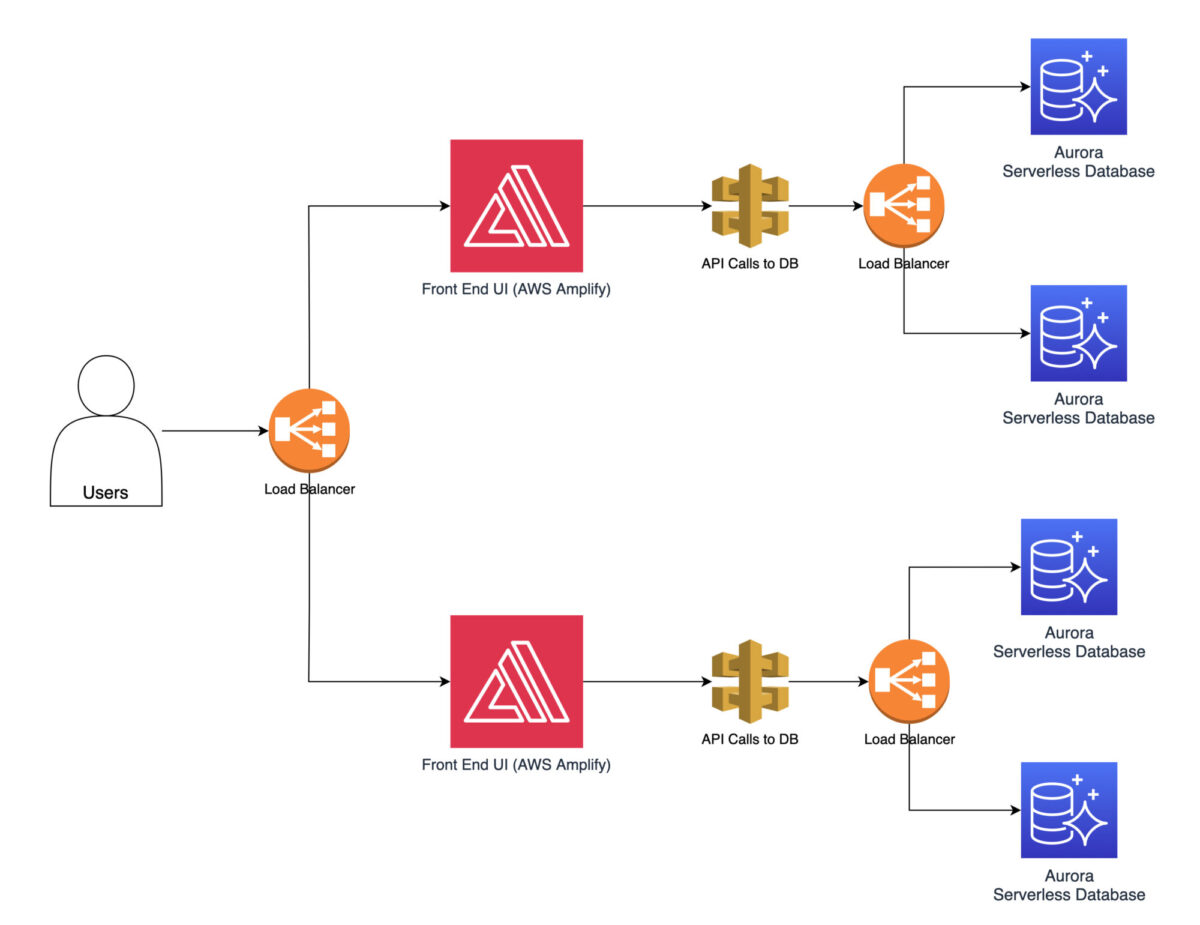
When designing the architecture, you should consider load balancing as many parts of the system as possible.
Systems are only getting more complex over time.
You cant predict how it will evolve in the course of the next several years.
AWS offers Elastic Load Balancing (ELB) services that automatically distribute incoming traffic to multiple instances.
Load balancing helps prevent any single resource from becoming overwhelmed, thus improving system performance.
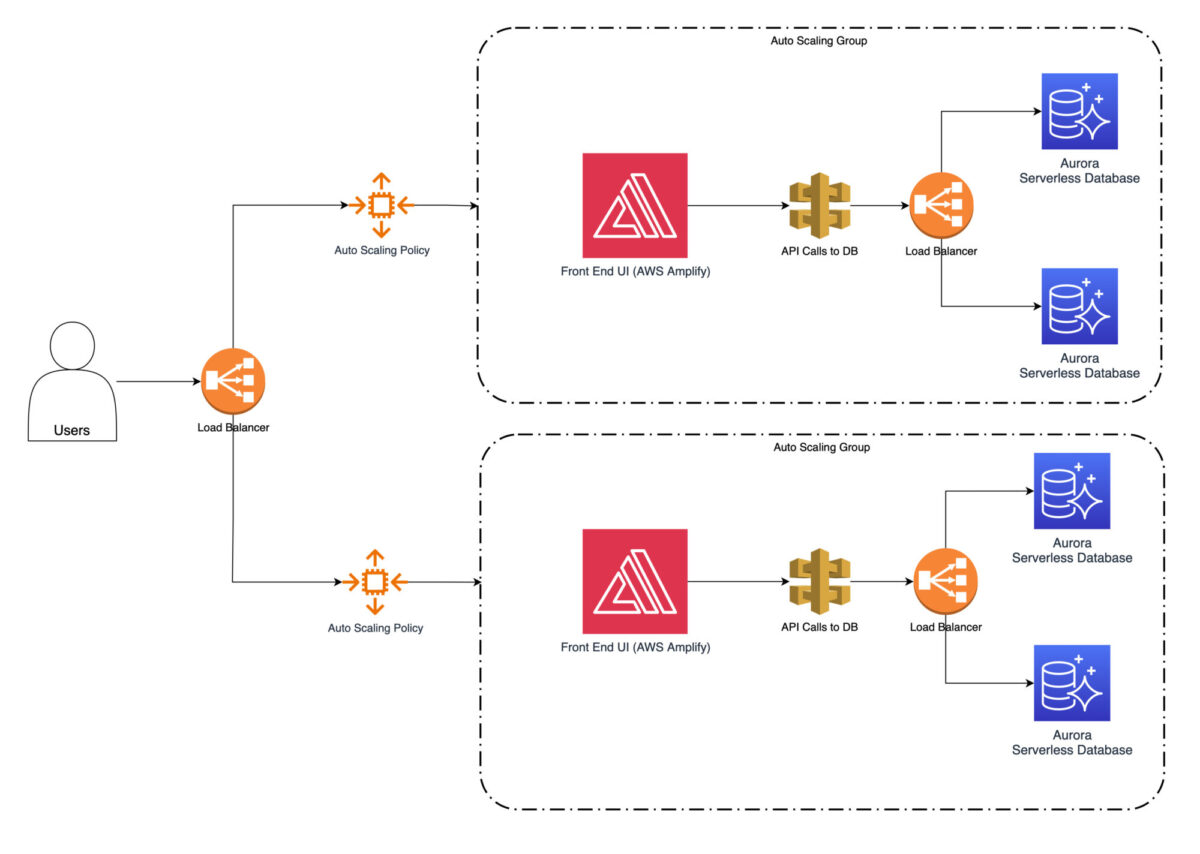
It can go both ways upwards and downwards.
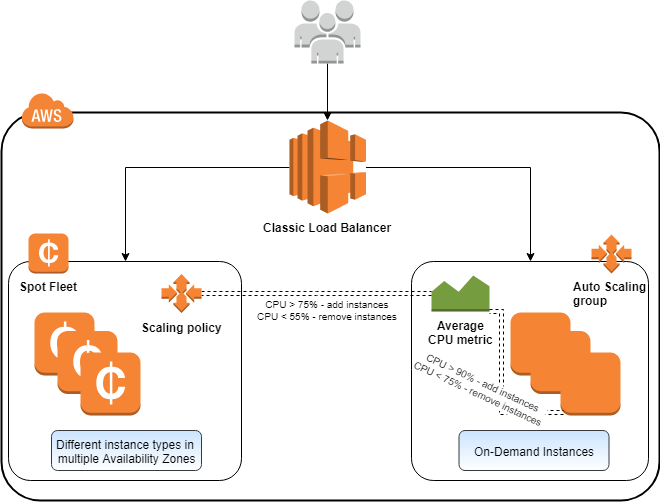
AWS Auto Scaling is a specific functionality not every major cloud provider has, even today.
you’re able to define scaling policies that automatically add or remove instances based on predefined conditions.
Vertical scaling is also possible.
The good thing is that once set, you dont need to sit and watch the scaling processes.
They will automatically adjust.
After that, you wont pay for additional instances when they are not necessary.
Also, you wont process the data too long if there is a load peak.
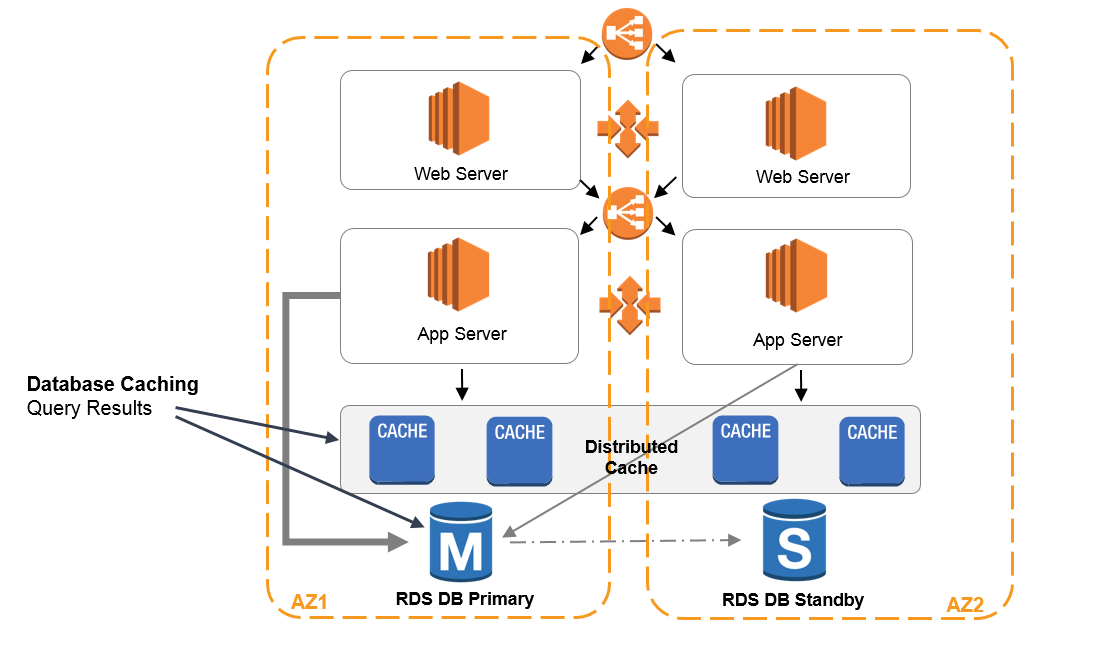
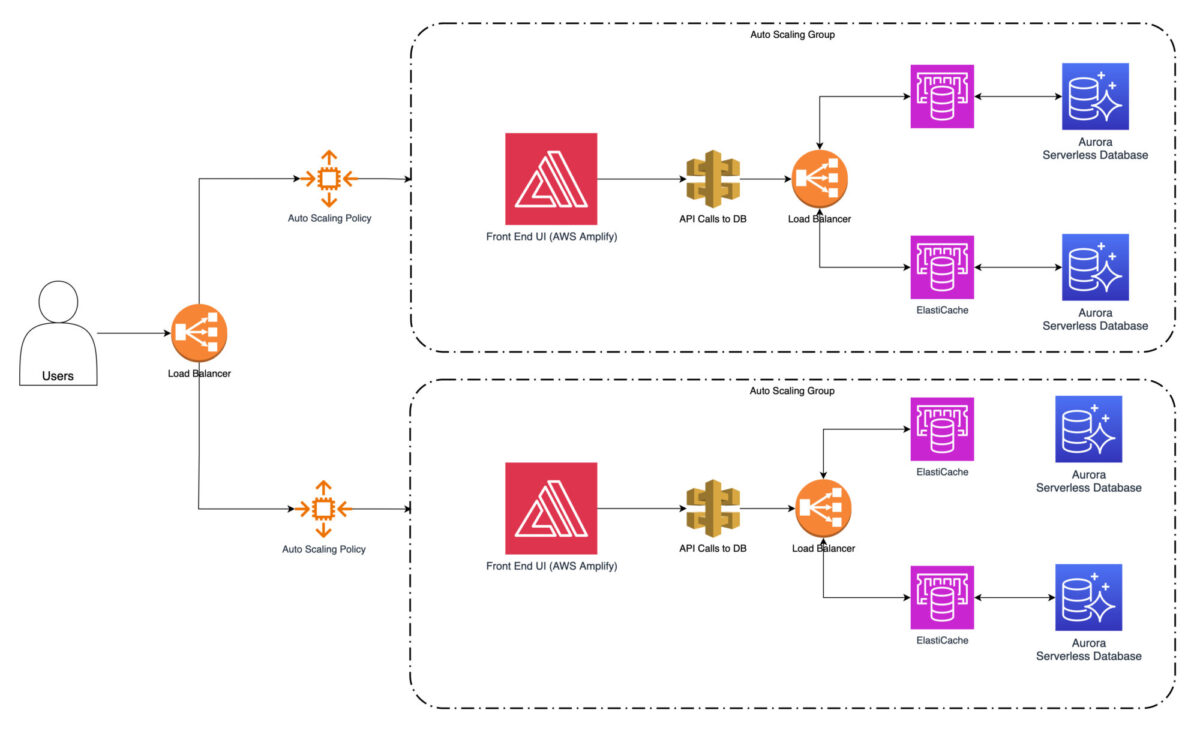
Amazon Web Services contains Amazon ElastiCache web service.
Its a fully managed in-memory caching service that supports popular caching engines like Redis and Memcached.
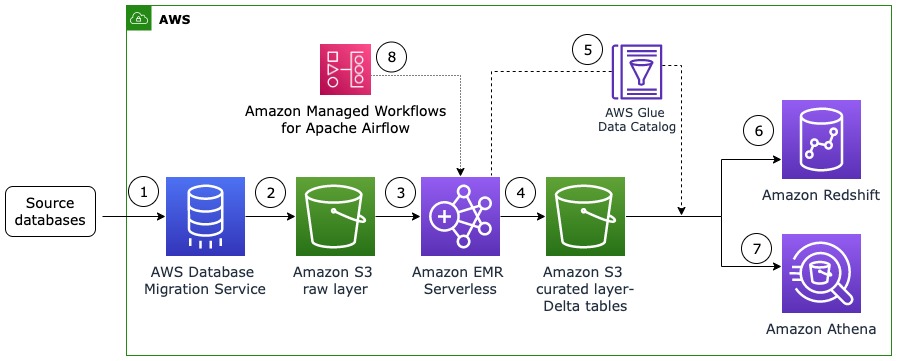
Usually, the final choice is between full data load and incremental data load.
This is what I can see the project teams tend to do often.
This approach is very suitable for initial data synchronization or when you simply need to refresh the entire dataset.
However, it can be time-consuming and resource-intensive.
Sometimes, it is still the best strategy.
For example, if the data on the source is frequently changing dramatically.
In this case, it absolutely makes sense to implement the full data load process.
And what if you scheduled to execute the loading process every hour or even more frequently?
Incremental data load strategy results in faster synchronization and improved performance metrics.
It is ideal for scenarios where frequent updates occur.
However, Incremental load usually requires a much more sophisticated approach.
Theres also a much higher chance that you miss some portion of the data changes during the processes.
This mostly happens if the source system is outside of your platform and direct responsibility.
In that case, obviously, you cant have full control over processes that happen in the source system.
Otherwise, you might not be getting the full set of last data increments.
And maybe you dont even know about that.
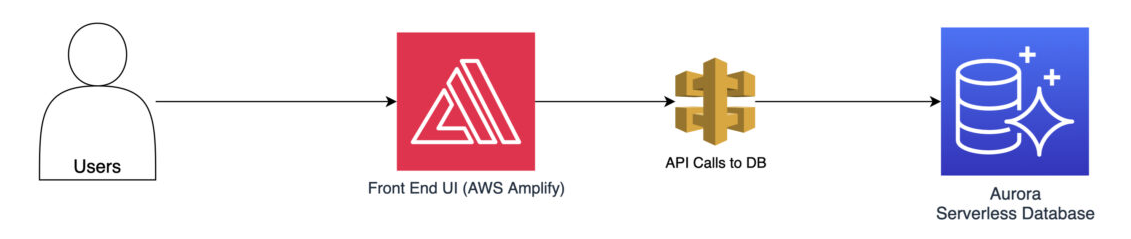
Imagine a popular shopping website hosted on AWS.
Potentially, it can even cause sporadic downtimes.
As a first step in performance optimization, you might implement load balancing using AWS Elastic Load Balancer.
This ensures that you distribute incoming traffic evenly across multiple instances.
This prevents the instances from becoming overwhelmed.
This ensures that the website can handle the increased traffic and maintain optimal performance.
Frequently accessed data, such as product information or user preferences, can be cached.
It will greatly reduce the need to fetch it from the database services repeatedly.
This significantly improves response times and overall operating system performance.
As your platform evolves, you should revisit the AWS architecture regularly.