We earn commission when you buy through affiliate links.
This does not influence our reviews or recommendations.Learn more.
Linux is an excellent choice of operating system until you stumble upon an error.
It is not you; it is how users deal with Linux, which requires constant learning and troubleshooting.
Linux comes with plenty of amazing package managers.
Thats why, in this guide, well learn how you’re free to solve the error.
Throughout the guide, well be using Ubuntu.
What is the E: Unable to locate package Error?
The error is clear, and you’re able to understand it yourself.

It simply means that Linux cannot find the package youre trying to install.
The good news is that there are solutions for this kind of problem.
Youll use the default APT package manager when installing a package in Ubuntu.
You might use apt-get or apt to implement the package.
The command to do so is as follows.
If everything works fine, youll not see any errors.
The package will install as intended.
However, sometimes, you get the E: Unable to locate package package_name.
The output looks like the one below.
When the error occurred, Linux failed to locate the package.
So, it is up to us to fix the issue and ensure it doesnt happen again.
Before trying to fix it, you must know the reasons.
#1.Package Name Did You pop in It Correctly?
One of the common mistakes that Linux users make is to not bang out the package name correctly.
So, if you make a simple typo, Ubuntu will throw the error.
Lets check an example when installing Gimp an image processing tool.
As expected, youll get the E: Unable to locate package gump.
After all, there is no package gump out there.
A typo can happen more often than you think.
So, if you take a stab at install gimp by naming it Gimp, itll still fail.
So, the only way to install gimp is to throw in the package name correctly.
But what if you should probably know the package name correctly?
In that case, you’re able to use the apt search command to look for it.
#2.Update Package List/Repository Cache
Ubuntu interacts with the repositories differently.
Rather than downloading the whole respiratory, it builds a local cache.
The local cache contains the list of available packages.
When you run sudo apt update, Ubuntu creates a local cache.
Once you execute the apt-get install command, the APT Package Manager will search the cache for the package.
As the cache is not built with the latest information, installing even standard packages can cause an error.
In some cases, the cache can need to be updated.
And, then you have to update it using the apt update command.
You should also clean the cache before updating it.
To do so, launch the following command.
So, whats your options?
Youll need to learn about the Universe repository to understand your options.
Generally, the Linux system doesnt enable it by default, which can lead to an error.
Or the Ubuntu version youre running doesnt have access to the package youre trying to download and install.
To check whether your Ubuntu is not outdated, youll first need to check its version.
you’re able to do it by running the following command.
Im using the latest stable 22.04 LTS version with the codenameJammy.
Excellent; note them down and then head to theUbuntu packageswebsite.
On this page, you’ve got the option to manually search for packages.
It has a nifty Search section where you’ve got the option to search by entering a keyword.
The keyword can be the package name or anything that can help you pinpoint the package.
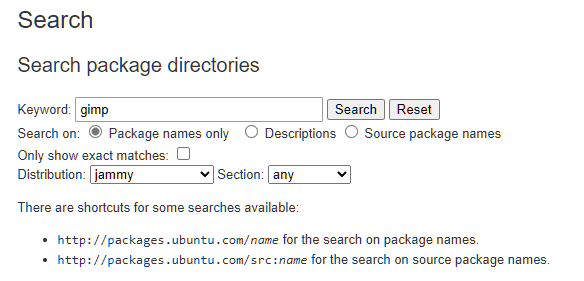
So, now, all you better do is enter the package name and press the Search button.
As gimp is a known package, we get an exact hit.
And, if you carefully notice, youll see that it is available in the Universe repository.
Now, youre sure the package is available for your Ubuntu version.
Next, youll need to fire up the repository.
To switch on the repositories, execute the following command.
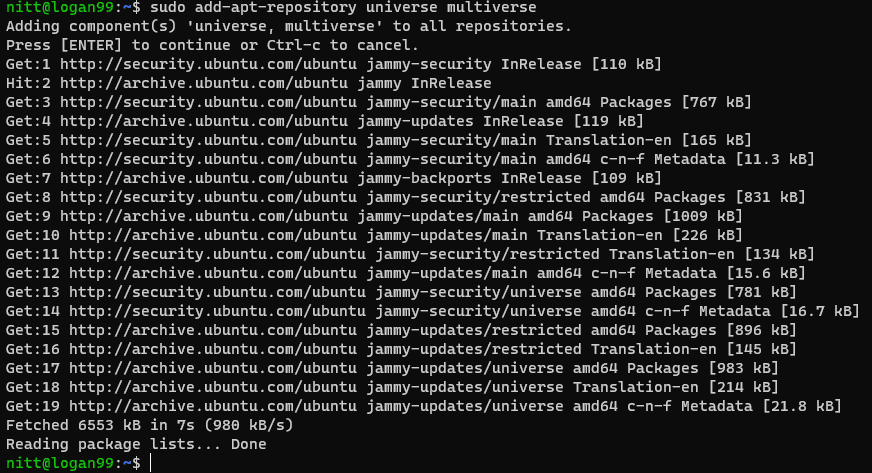
The above command enables the universe and multiverse repository.
Once thats done, confirm to rebuild the cache again.
you might also install other repositories, such as main and restricted.
fire off the following command to do so.
But what if the package is not available for your Ubuntu version?
In that case, youll have to use third-party repositories such as PPA.
To check whether your Ubuntu is still supported, trigger the following command.
If your Ubuntu version is not supported, you only need to upgrade to the latest LTS version.
The file contains all repository-related data.
Youll need to dive into the/etc/apt/sources.list file.
Generally, you must see if the repository links are active and match the official listing.
To check, visit the official distros site and look for the information.
Conclusion What if Nothing Works?
Before you do so, its best to try all your possibilities.
you’re able to find them through a third-party personal repository (PPA).
Generally, they offer a direct way to download the package files.
If everything fails, then its best to look for alternative apps.
Next, check out the bestexamples of the find command in Linux.