We earn commission when you buy through affiliate links.
This does not influence our reviews or recommendations.Learn more.
Microsoft Excel, a powerful spreadsheet tool, has become an indispensable tool in various industries across the globe.
However, even the most reliable software can encounter occasional glitches, and Excel is no exception.
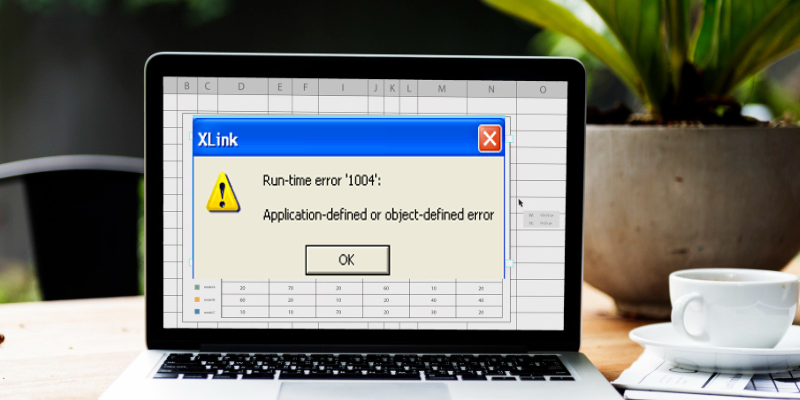
One such common issue that Excel users often face is the dreaded Run-Time Error 1004.
This error can be frustrating and hinder your productivity.
Resolving the Run-Time Error 1004 promptly is crucial for Excel users to ensure a smooth workflow.
Additionally, well share a few tips to help you avoid encountering this error in the future.
So, lets dive in!
What is Run-Time Error 1004?
It is usually accompanied by a message that says, utility-defined or object-defined error.
After researching through different community platforms, we have found the common causes include:
1.
These conflicts may arise due to compatibility issues or overlapping functionalities.
These errors can occur when writing or modifying macros or when copying code from different sources.
Identifying the specific cause of the error is essential to resolve Run-Time Error 1004 effectively.
Our experts have tested each method mentioned below.
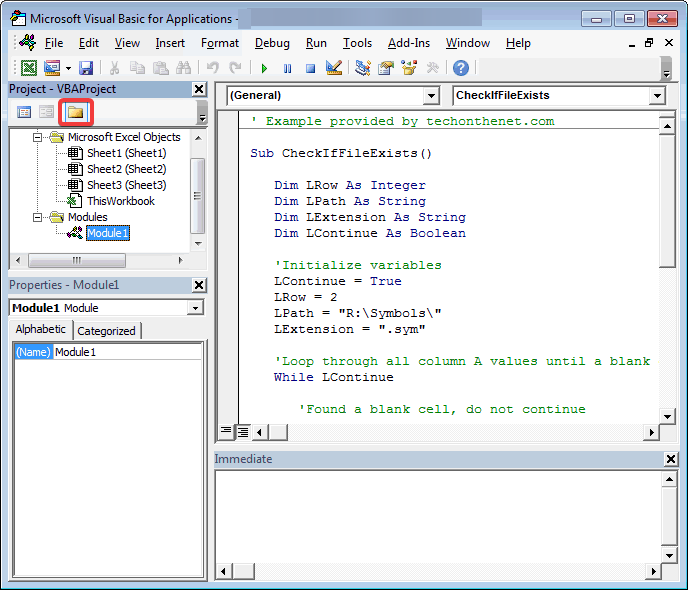
Making necessary adjustments to the macro code can often patch up the error.
Check how to review macro code and make improvements.
1.kick off the Excel workbook that contains the macro you want to review.
2.PressAlt + F11on your keyboard.
This will kick off the Visual Basic for Applications (VBA) editor.
3.In the VBA editor, locate the project explorer window on the left side of the screen.
It typically shows a list of workbook names and modules.
This will display the modules within the workbook.
5.Double-snag the module that contains the macro code you want to review.
The code editor window will open, displaying the code.
7.Press theF8key on your keyboard.
This is the shortcut for going through the code line by line.
8.The highlighted line of code will be executed, and the next line to be executed will be highlighted.
9.Continue pressingF8to step through the code line by line.
A red dot will appear, indicating the breakpoint.
11.While reviewing the code, pay attention to any error messages that appear in the VBA editor.
if you catch any errors, take note of the line number and the issue notification.
you might use this information to troubleshoot and fix any issues.
This process helps identify any errors or areas of improvement in the code.
If you have Microsoft Work installed on your rig, try uninstalling it and peek if the error persists.
To uninstall Microsoft Work follow the below steps.
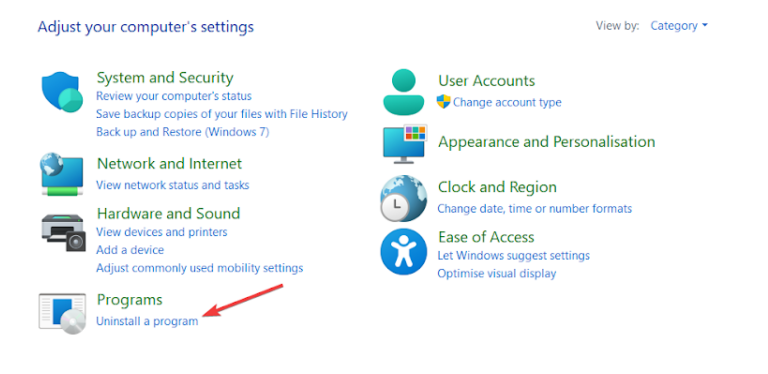
1.fire up the Control Panel on your gear.
2.Select Programs and click Uninstall a program.
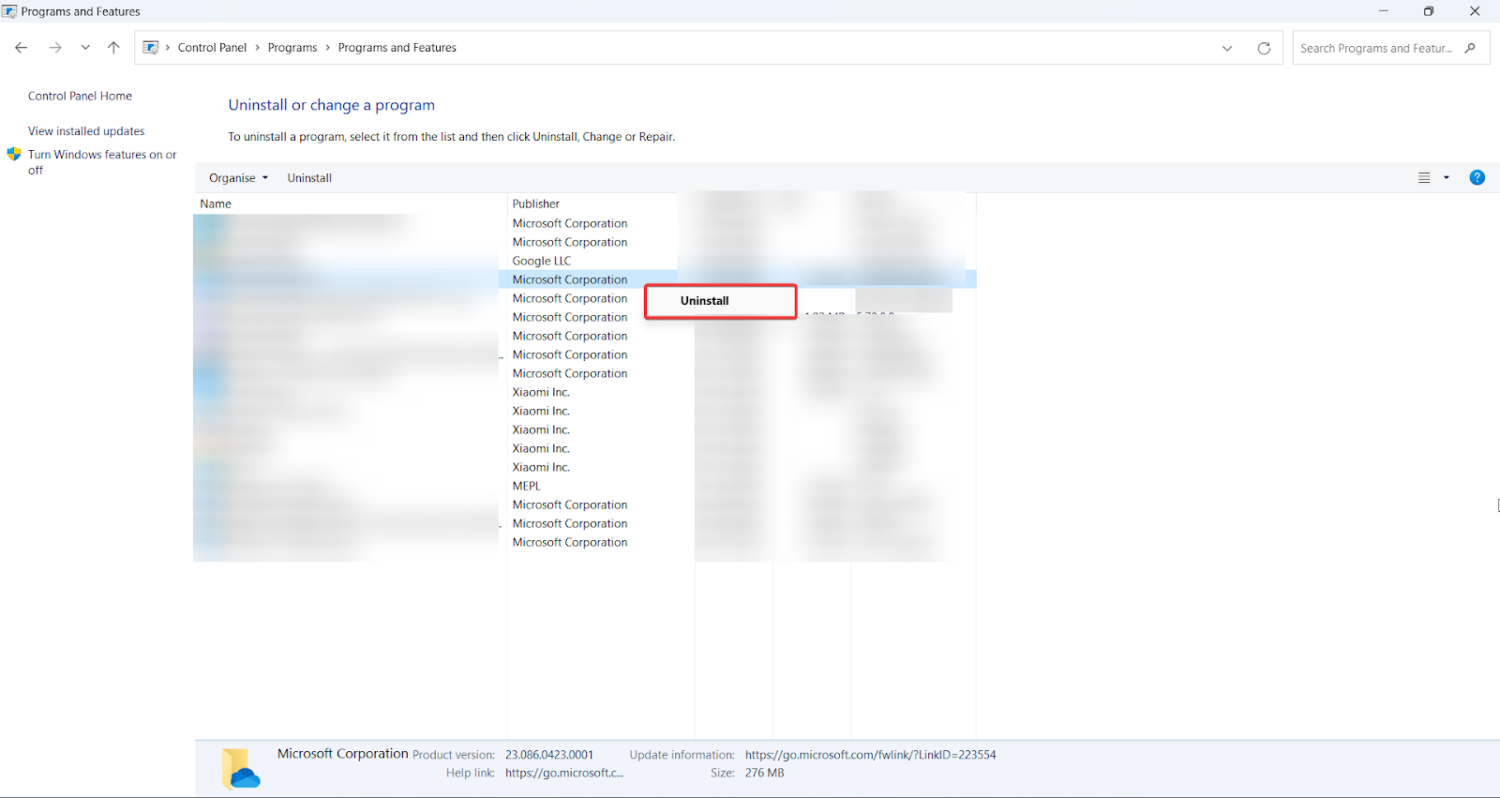
3.Locate Microsoft Work in the list of installed programs.
4.punch Uninstall and follow the on-screen instructions to remove Microsoft Work from your system.
To fix this issue, delete any existing GWXL97.XLA files.
Here is the step-by-step process to delete GWXL97.XLA files.
2.Look for any GWXL97.XLA files in the folder.
3.grab the files and delete them.
4.Restart Excel to see if the error is resolved.
Send the diagnostic report to Microsoft and let it repair Excel on your system.
you’re able to also repair it manually from Control Panel.
If repairing doesnt work, you might uninstall and reinstall Excel to ensure an error-free installation.
- launch the Control Panel on your machine.
Select Programs and choose Uninstall a program.
Locate Microsoft Office in the list of installed programs.
- choose Change or Repair and follow the on-screen instructions to repair your Office installation.
Alternatively, uninstall Microsoft Office completely and reinstall it with a fresh installation.
Tips to Avoid Run-Time Error 1004 in The Future
Prevention is always better than cure.
Here are a few tips to help you avoid encountering runtime error 1004 in the future:
1.
Validate Input Data:Ensure that the data you are working with is valid and properly formatted.
Implement data validation techniques to minimize the chances of encountering errors due to invalid or corrupted data.
Pay close attention to error handling and ensure that your code can gracefully handle unexpected scenarios.
These updates often address known issues and can help prevent runtime errors.
Monitor System Resources:Keep an eye on your computers memory and system resources.
Avoid running resource-intensive applications simultaneously with Excel to prevent memory-related errors.
Close unnecessary programs or cycle your machine if you catch slow performance or frequent errors.
5.Regular updates and maintenance for Excel: Regularly update and maintain Excel, including any associated add-ins or plugins.
Stay up-to-date with the latest software patches, security updates, and bug fixes provided by Microsoft.
These updates often address known issues, enhance performance, and improve compatibility with other software.
Avoid excessive reliance on complex formulas or nested functions that can be hard to troubleshoot.
2.Break down complex tasks into smaller, manageable subtasks.
Use modular programming techniques to divide your code into reusable functions or procedures, promoting code reusability and maintainability.
3.Comment on your code effectively to provide clear explanations and document the purpose of each section or function.
This helps you and others understand the codes logic and facilitates future modifications or debugging.
4.Regularly back up your Excel files and macros to ensure you have a copy in case ofdata lossor corruption.
Consider using version control systems or cloud storage services for added protection.
If you have further queries, drop us a comment.
You may also explore MS Excel Formulae to master data analysis.