We earn commission when you buy through affiliate links.
This does not influence our reviews or recommendations.Learn more.
You have heard about them before.
You use it whenever you attempt to download, install, remove, or update a package on Ubuntu.
So, does Ubuntu keep all of them in your OS?
Or a remote place?
What are Ubuntu Repositories?
Ubuntu repositories are software archives maintained by Ubuntu.
The repositories contain hundreds and thousands of software.
All of these are accessible to the general users.
it’s possible for you to also think of repositories as software archives.
Repositories aim to provide a secure, centralized place to access software for your needs.
These Ubuntu repositories follow strict rules when adding software.
Each software is tested thoroughly with the Ubuntu version before making it available on the repository.
As Ubuntu is Debain-based, it uses an APT package manager to handle the packages.
The packages are in .deb format, containing the libraries and programs you better run your tasks.
In Linux, youll find different package formats for different flavors.
For example, you have DEB packages for Debian, whereas RPM is for RHEL-based distros.
As Ubuntu uses an APT package manager, you must use the apt command to install software in Ubuntu.
Lets learn more about package managers to understand how Ubuntu repositories work.
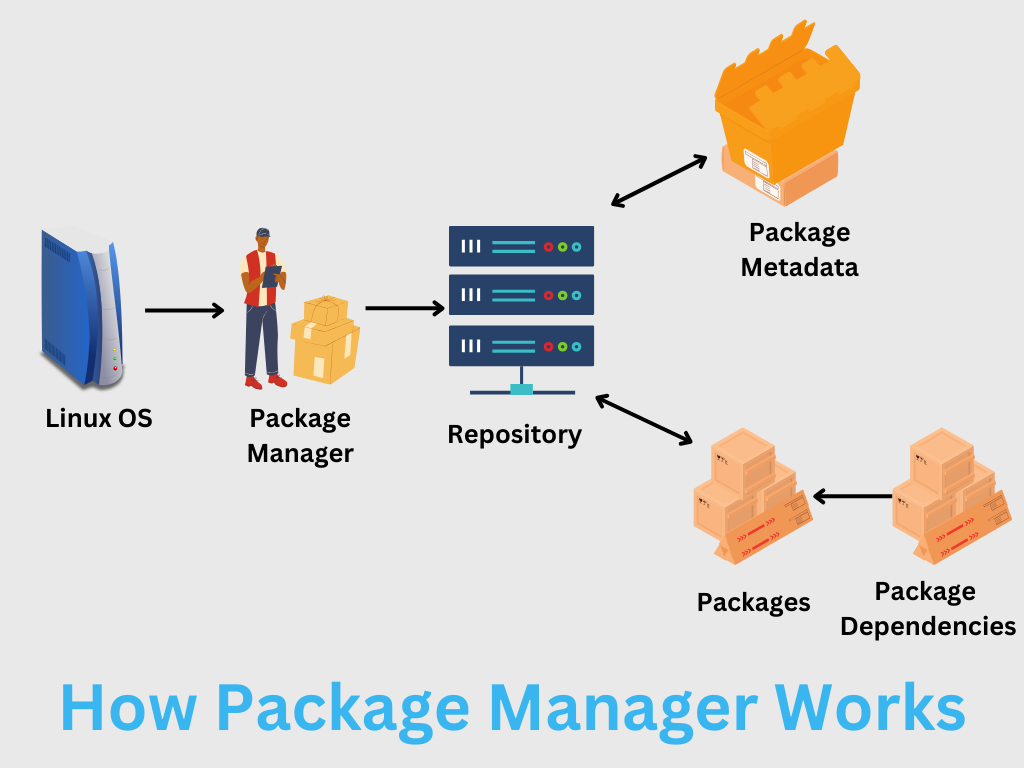
How Does Ubuntu Repository Works With Package Manager?
To understand the Ubuntu repository, we must look at how the package manager works.
A package manager is a set of software that lets you manage packages on your Linux distro.
This leads us to the concept of repositories.
The repositories are a virtual place that lists all the packages.
Here, each package has its metadata information.
Using a local cache removes the need to connect to the remote repository every time you run a command.
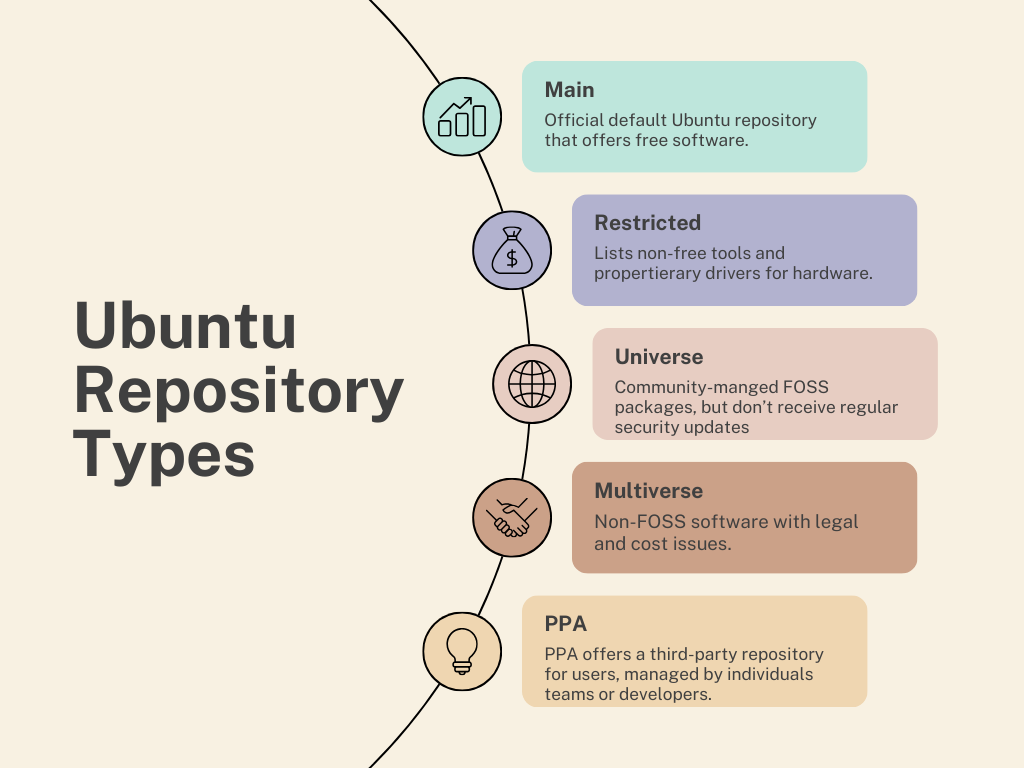
Types of Ubuntu Repositories
Ubuntu repositories are divided into four main categories.
These include:
Generally, an average needs to learn about them.
#1.Main
The Main Ubuntu repository is the home of free software.
Any software listed here is free to redistribute.
Also, the Ubuntu team supports the free software.
All these make the Main component popular, giving users access to popular open-source apps.
Community, users, and Ubuntu developers maintain the main repository software list.
They hand-pick the software to provide value to the end users.
Also, each software receives security updates alongside Canonical technical support.
Note:This is also enabled by default when you first install Ubuntu.
#2.Restricted
The Restricted component deals with non-free tools and drivers.
#3.Universe
The Universe repository hosts free and open source software.
However, unlike the Main repository, you wont get regular security updates as Ubuntu doesnt manage it.
Hence, the Universes repository is maintained by the community.
As Ubuntu is community-driven, you get access to thousands of excellent software.
#4.Multiverse
The Multiverse repository component deals with the non-FOSS software.
you’re able to access non-free software with legal and licensing costs or issues here.
They offer an easy way to get packages unavailable via other repository types.
Lets look at both methods below.
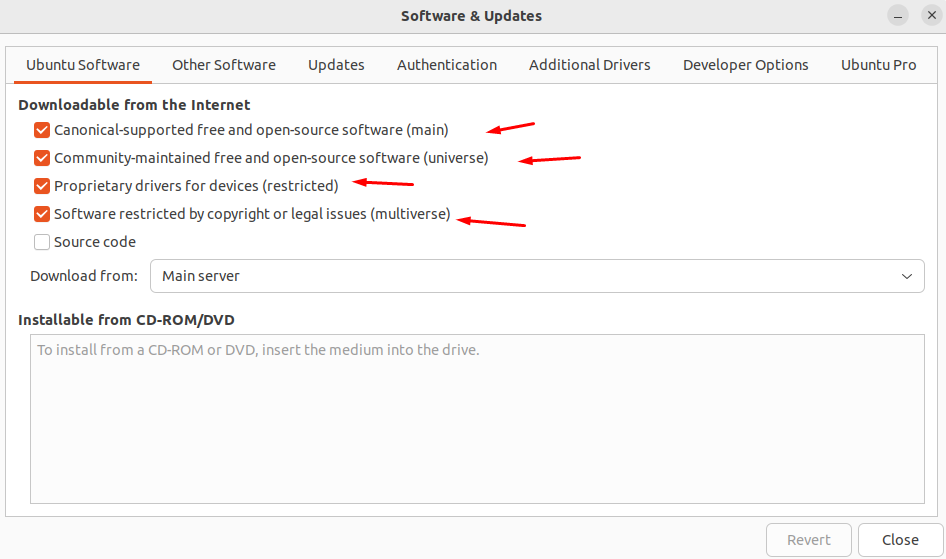
it’s possible for you to access it by searching or accessing Applications > Software and Updates.
By default, all four repositories are enabled.
it’s possible for you to turn these options on/off and close them for it to take effect.
To enable them, execute the following command(s).
you’ve got the option to also enable all four of them in one command.
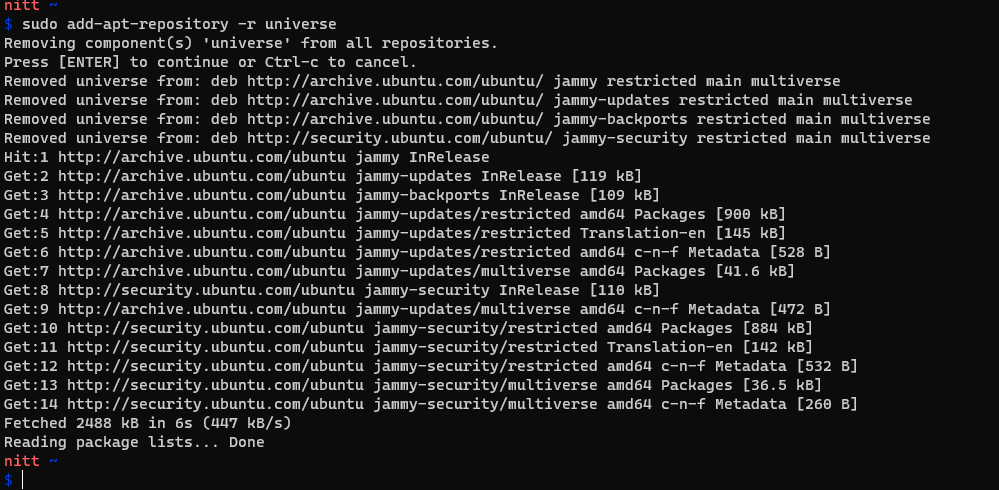
If you want to remove the repository, you better trigger the same command with the -r argument.
For example, check the command for removing the Universe repository.
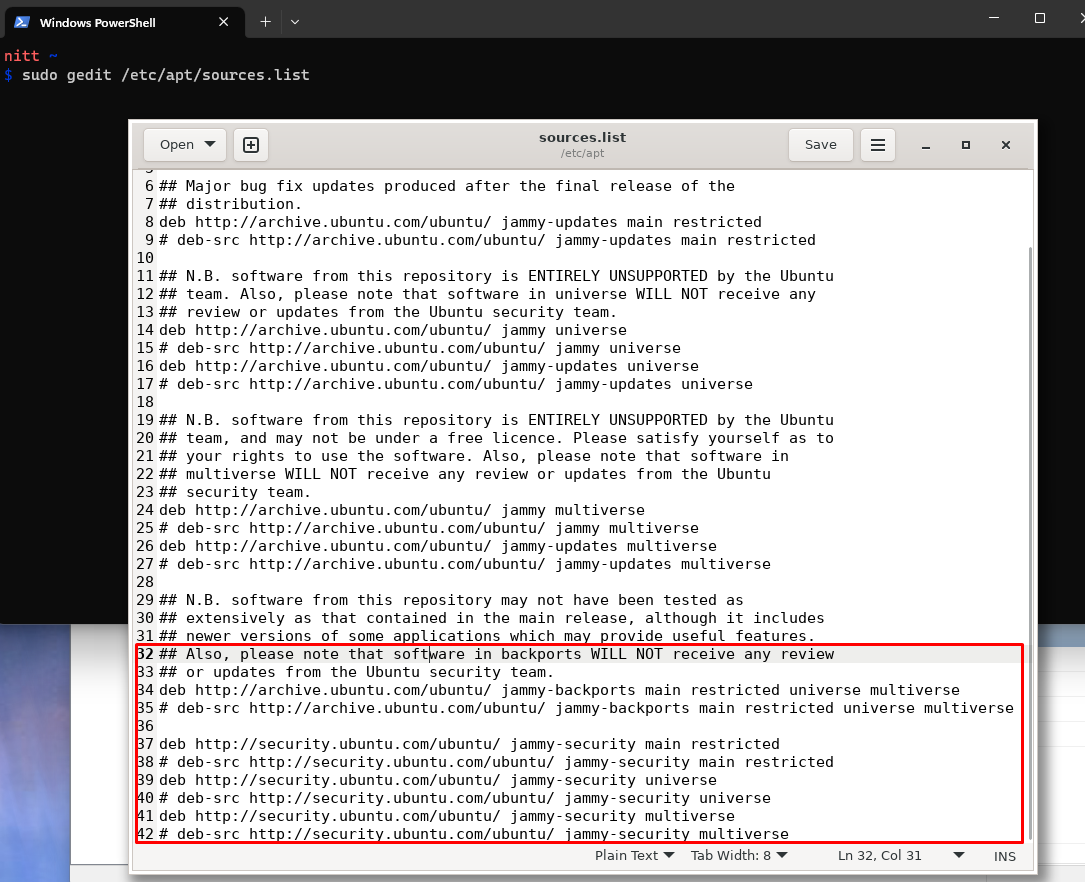
For disabling/deleting, youll need to edit the sources.list file or use the graphic interface method.
you’re able to edit the sources.list file by running the following command.
PPA is created and managed by individual teams or developers to provide a central software repository for users.
They offer benefits over traditional repositories with improved compatibility, faster updates, and unofficial package support.
However, if you want more reliability and trust, nothing beats Ubuntu repositories, which are managed officially.
To use PPA, you better add it to your systems repository list.
Also, there are two types of PPA: official and unofficial.
Canonical or other trusted organizations manage the official PPA repositories.
These official PPAs are considered safe to use.
On the other hand, the unofficial PPA repositories are not affiliated with Ubuntu in any form or way.
This means 3rd-party organizations and individuals create them making them unreliable.
Ubuntu Repositories Commands
In this section, well summarize the different commands for repositories.
List of Repositories
To list all the repositories on your system, execute the following command.
The repository file is sources.list, located at/etc/apt/folder.
However, you might find it in other locations:/etc/apt/sources.list.d/folder.
Adding New Repositories
As discussed earlier, you might add a repository by running the apt-add-repository command.
It differs from add-apt-repository, which requires you to provide the Repository name as input.
Youll need to enter the repository address, associated version, and branch here.
Also, when you add a repository, you might have to install its GPG security key.
Removing Repositories
Removing repositories can be done by using the following command.
you might do it by using the following command.
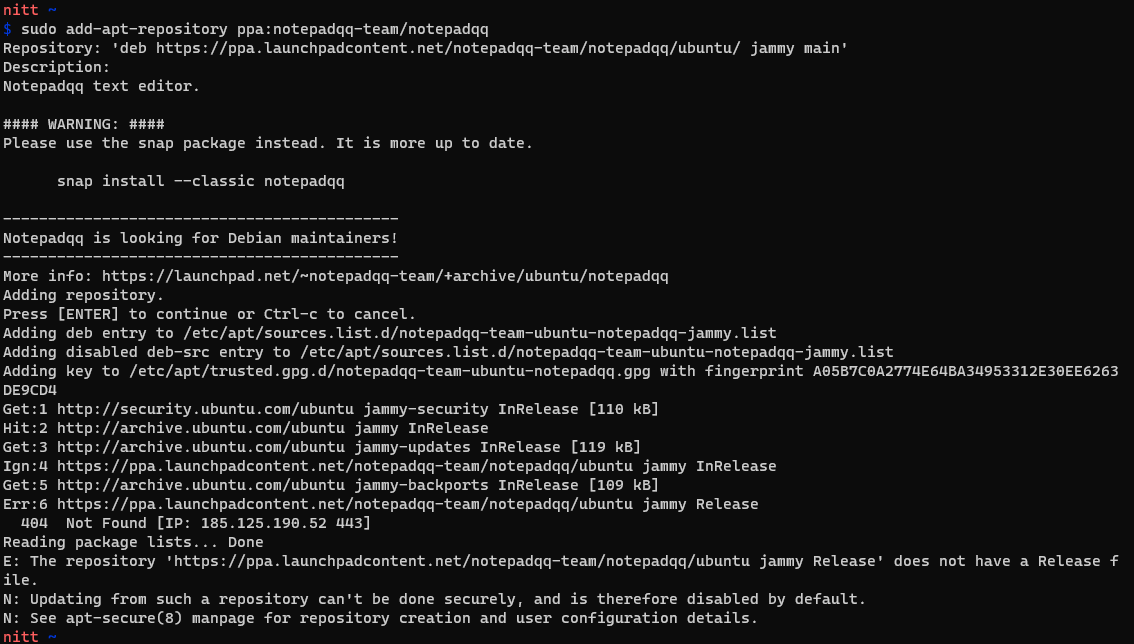
Once done, you could add the PPA repository using the following command.
So, if you want to add notepadqq PPA, you oughta trigger the following command.
Similarly, you’ve got the option to remove a PPA using the following command.
Conclusion
Ubuntu is an excellent Linux distro.
It provides new users with an easy way to introduce themselves to the world of Linux.
The Ubuntu repositories are a fine example of how Ubuntu manages packages along with its own APT package manager.
Now that you understand entirely how Ubuntu repositories work, you could now customize them to your needs.
Next, check out our detailed article onUbuntu PPA and how to install it.