We earn commission when you buy through affiliate links.
This does not influence our reviews or recommendations.Learn more.
For example, a self-driving car AI could begin by navigating simple routes with minimal traffic.
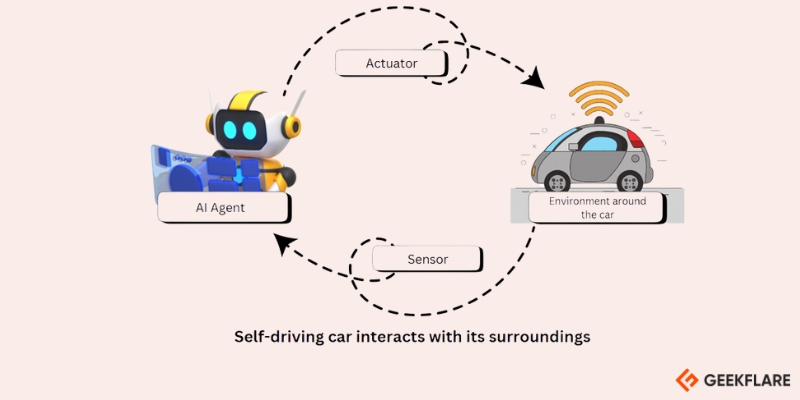
AI agents are like a smart assistant that learns and adapts over time.
They can handle different tasks, make decisions on their own, and improve as they go.
How AI Agents Work?
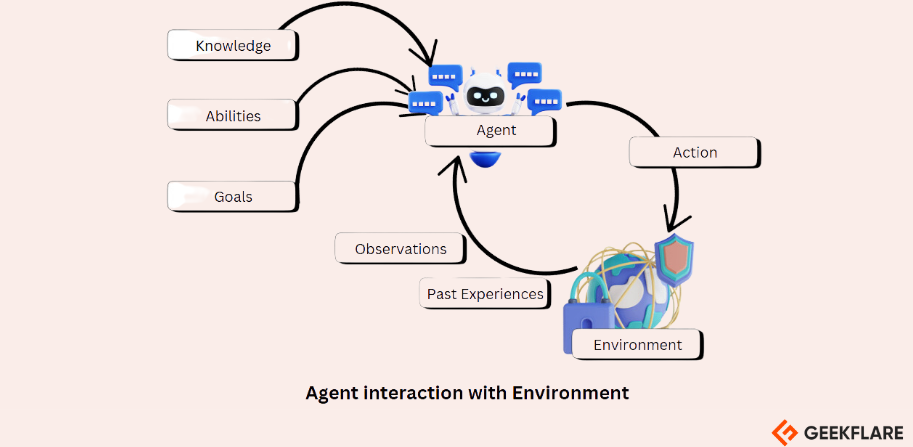
AI agents are powered by large language models (LLMs), often referred to as LLM agents.
This allows the agent to adapt to user expectations over time.
AI agents operate through architecture that involves three main components: Perception, Decision, and Action.
Heres a simple breakdown of how these work together and why AI agents are useful for modern applications.
Perception: This is how the AI agent sees or senses its surroundings.
This input data is necessary for the agent to understand its current situation and make relevant decisions.
Action: After making a decision, the agent performs the chosen action.
AI agents are constantly in touch with their environment, adapting their actions based on changing data.
Each decision informs the next, allowing it to navigate safely and efficiently even in changing traffic.
Types of AI Agents
AI agents can be classified based on their intelligence and capabilities.
Here are the key types:
1.
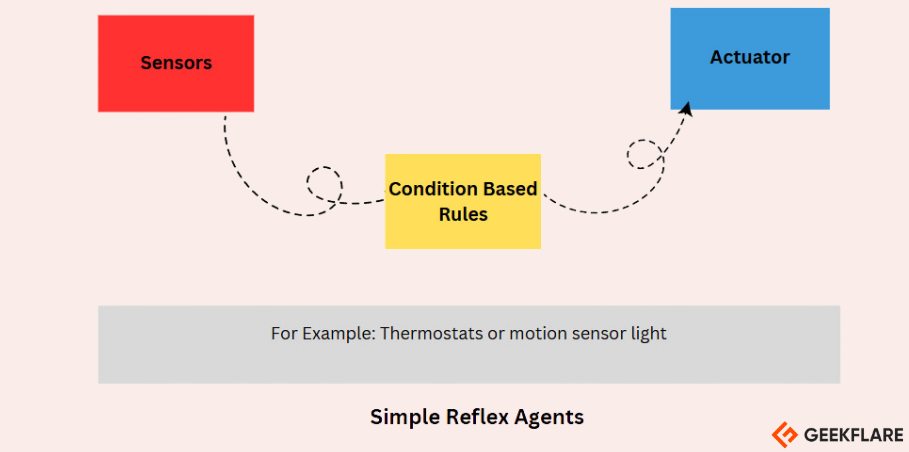
Simple Reflex Agents
Simple reflex agents act based on the current percept and use condition-action rules.
They do not consider past actions or the broader context of the environment.
These agents are limited in intelligence and can struggle in partially observable environments.
They may fall into infinite loops if the environment changes unexpectedly.
For Example, An AI agent in the AC system operates based on simple condition-based rules.
The AI agent constantly monitors the temperature of the environment (Room) and simply applies these rules.
The AI doesnt require complex reasoning or memory.
It only reacts based on the current temperature readings.
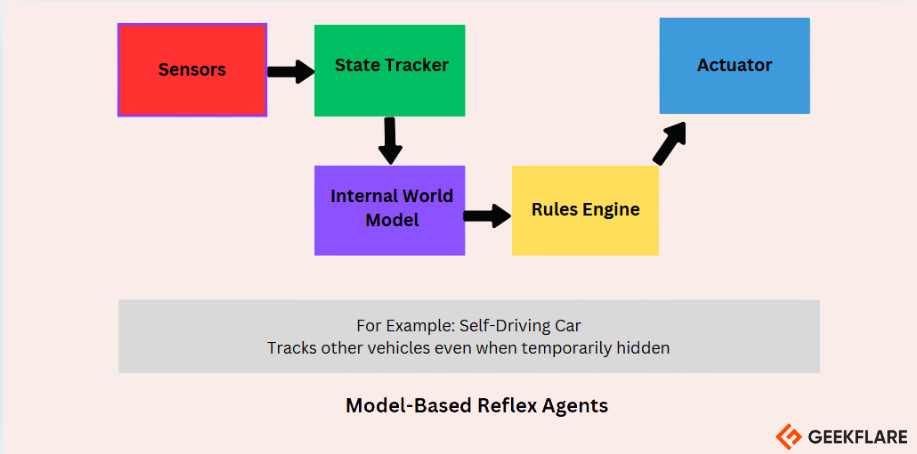
Model-Based Reflex Agents
A model-based AI agent works by using rules to match its actions to the current situation.
The state tracker keeps the car updated on its current position and situation.
Finally, the actuator carries out these actions by controlling the cars steering, brakes, and acceleration.
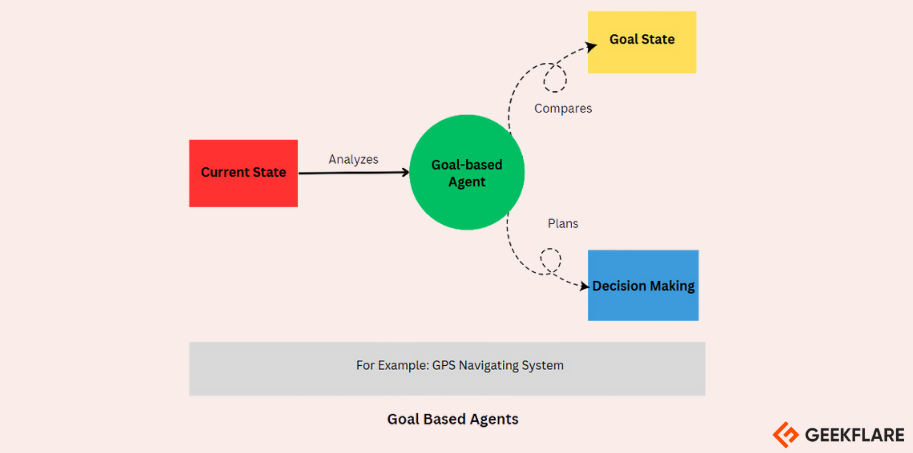
Goal-Based Agents
Goal-based agents make decisions with the aim of achieving specific goals.
Their actions are planned to reduce the distance between the current state and the desired goal.
For example, a GPS navigation system finds the best route to a destination.
It compares the two to figure out the best route.
The agent then makes decisions on directions to help reach the destination.
It keeps checking the current position against the goal and adjusts the route if needed.
The goal-based agents purpose is to guide the user from start to finish by following the plan.
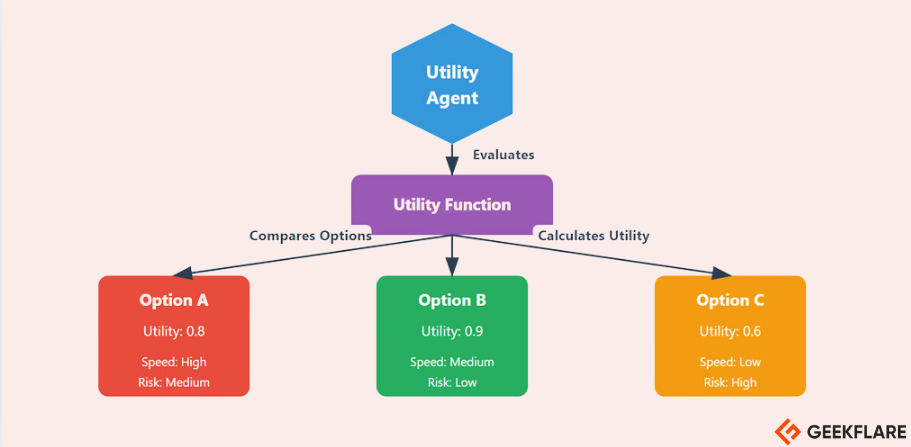
Utility-Based Agents
Utility-based agents evaluate multiple alternatives by considering which one offers the highest utility or satisfaction.
They choose actions that maximize their overall happiness or efficiency, such as choosing a faster or safer route.
These agents prioritize actions based on their utility function, which measures how well a goal is achieved.
For Example, a Stock trading bot evaluates options to choose the best one.
The environment is the stock market, where the bot assesses various investment opportunities and market factors.
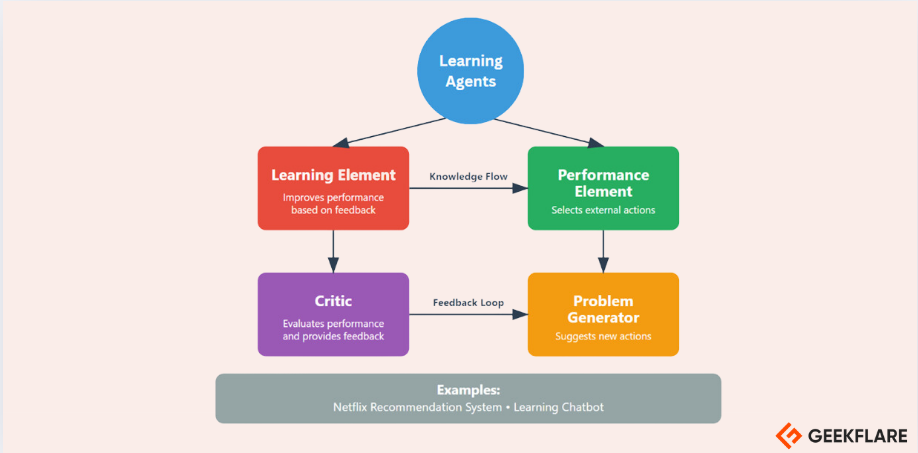
Learning Agents
A learning agent in AI is designed to improve by learning from its experiences.
It starts with basic knowledge but can adapt and become more effective.
This key in of agent has four main parts.
The learning element helps it learn and improve by interacting with its surroundings.
The critic gives feedback on the agents performance, guiding it to meet certain standards.
Together, these parts unlock the agent to learn and adapt independently.
The Performance Element uses this information to decide what shows or movies to display on the users homepage.
Altogether, this process helps Netflix continuously refine its recommendations based on user behavior.
For example, a robot may use cameras to detect obstacles, or a chatbot may receive customer queries.
Action
Once an agent senses its environment, it must take action to achieve its goals.
This is done through actuators, which allow the agent to interact with its environment.
For example, moving a robotic arm, sending a message, or updating a display.
The choice of action is determined by the agent function, which maps sensed inputs to specific actions.
Reasoning
Reasoning is the process that allows an agent to make intelligent decisions.
Learning agents modify their behavior based on feedback from their environment.
Applications of AI Agents
AI agents are being used across various industries, driving innovation and automation.
Machine learning helps these agents enhance their performance by learning from experiences and varying road conditions.
In factories, they guide robots in jobs like assembly and welding, adjusting as needed.
In healthcare, AI robots assist in surgeries, help with medications, and even provide companionship.
These robots use sensors to understand their surroundings, make decisions, and carry out actions.
Over time, they can learn from experience, becoming better at their tasks and decision-making.
Through AI, NPCs can adapt to different play styles, making each gaming session unique.
Customer Support (Chatbots)
AI chatbots are transforming customer service by providing quick assistance to users.
Reduced Cost
By automating tasks, AI agents help businesses cut costs.
For example, AI can analyze financial data to spot fraud, preventing costly losses.
Informed Decision-Making
AI agents can process large amounts of data to uncover patterns that humans might miss.
This helps businesses make smarter decisions.
Improved Customer Experience
AI agents improve customer service by providing prompt and customized support to users.
Chatbots offer solutions to problems.
Adapt to individual preferences over time to give personalized suggestions.
Also, if the data used to train the AI is biased, the agent might make unfair decisions.
For example, an AI used in hiring might favour certain groups if the training data shows past biases.
Its important for developers to use diverse data and protect privacy to prevent these problems.
Dependence on Quality Data
AI agents depend on high-quality data to function accurately.
If the data is incorrect or incomplete, the AI can make errors.
Therefore, its essential to thoroughly clean and verify data to ensure the AI performs reliably.
For example, training an AI to understand human language needs powerful computers and GPUs.
This can be challenging for smaller companies due to high expenses.
Security Risks
AI agents connected to networks are vulnerable to cyberattacks.
To avoid this, strong security measures, like encryption and access controls, must be put in place.
To ensure AI agents are used responsibly, its important to address these challenges.
As AI technology improves, its important to keep improving the ways we handle these issues.
Check out thesebest AI agents for Businesses.
Interruption Capabilities
AI agents should be able to be interrupted when needed.
There should be a way to safely stop the agent without causing harm or disruption.
Unique Agent Identifiers
Assigning unique identifiers to each AI agent can improve security and accountability.
These IDs allow tracking of the agents actions and help identify who is responsible for the agents behavior.
Similarly, an AI handling stock trades might need human approval for large transactions.
Their ability to learn, adapt, and make autonomous decisions gives exciting opportunities for efficiency and innovation.